Ans: Unlike many other programming languages including C and C++, when Java is compiled, it is not compiled into platform specific machine, rather into platform-independent byte code. This byte code is distributed over the web and interpreted by the Virtual Machine (JVM) on whichever platform it is being run on. Thus when you write a piece of Java code in a particular platform and generated an executable code .class file. You can execute/run this .class file on any system the only condition is that the target system should have JVM (JRE) installed in it. In short, Java compiler generates an architecture-neutral object file format, which makes the compiled code executable on many processors, with the presence of Java runtime system.
A Wrapper class is a class whose object wraps or contains a primitive data types. When we create an object to a wrapper class, it contains a field and in this field, we can store a primitive data types. In other words, we can wrap a primitive value into a wrapper class object.
Why Wrapper Classes are needed:
- They convert primitive data types into objects. Objects are needed if we wish to modify the arguments passed into a method (because primitive types are passed by value).
- The classes in java.util package handles only objects and hence wrapper classes help in this case also.
- Data structures in the Collection framework, such as ArrayList and Vector, store only objects (reference types) and not primitive types. An object is needed to support synchronization in multithreading.
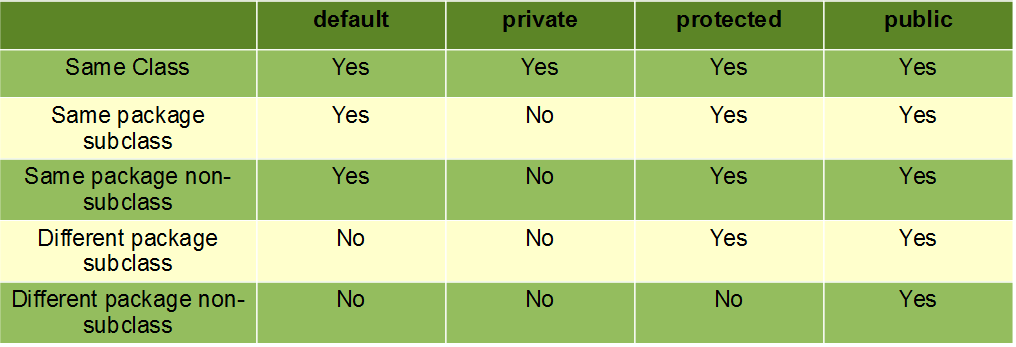
1. b) Mention the scope of all modifiers (public, private, protected).Write suitable program to illustrate the concept.
Ans:
2. a) What is method overloading? Can you override a private or static method in Java?Explain with an example.
Ans: If a class has multiple methods having same name but different in parameters, it is known as Method Overloading.There are two ways to overload the method in java
- By changing number of arguments
- By changing the data type
No, you can not override static method in Java, though you can declare method with same signature in sub class.Overriding depends on having an instance of a class.Since static method and private methods are bonded during compile time using Type of reference variable, and not object so the concept is not applicable.
Example:
class Parent {
static void display() {
System.out.println("Super class");
}
}
public class Example extends Parent {
void display() // trying to override display() {
System.out.println("Sub class");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent obj = new Example();
obj.display();
}
}Output:Example.java:10: error: display() in Example cannot override display() in Parent
void display() // trying to override display()
^
overridden method is static
1 errorAnd if display() method is set private it cannot be inherited to class example in the above example and shows the error of private access.
Ans:
| Abstract class | Interface |
|---|---|
| Abstract class can have abstract and non-abstract methods. From Java 8, it can have default and static methods also | Interface can have only abstract methods. |
| An abstract class may contain non-final variables | Variables declared in a Java interface are by default final. |
| Abstract class can have final, non-final, static and non-static variables | Interface has only static and final variables. |
| Abstract class can provide the implementation of interface. | Interface can’t provide the implementation of abstract class |
| Abstract class can be extended using keyword “extends” | A Java interface can be implemented using keyword “implements” |
| an abstract class can extend another Java class and implement multiple Java interfaces. | An interface can extend another Java interface only |
| A Java abstract class can have class members like private, protected, etc. | Members of a Java interface are public by default. |
//Creating interface that has 4 methods
interface A{
void a();//bydefault, public and abstract
void b();
void c();
void d();
}
//Creating abstract class that provides the implementation of one method of A interface
abstract class B implements A{
public void c(){System.out.println("I am C");}
}
//Creating subclass of abstract class, now we need to provide the implementation of rest of the methods
class M extends B{
public void a(){System.out.println("I am a");}
public void b(){System.out.println("I am b");}
public void d(){System.out.println("I am d");}
}
//Creating a test class that calls the methods of A interface
class Test5{
public static void main(String args[]){
A a=new M();
a.a();
a.b();
a.c();
a.d();
}} 3. a) Explain about FileReader and BufferedWriter class. How do you create own exception subclasses?Explain with an example.
Ans: Java FileReader class is used to read data from the file. It returns data in byte format like FileInputStream class. It is character-oriented class which is used for file handling in java.
Java BufferedWriter class is used to provide buffering for Writer instances. It makes the performance fast. It inherits Writer class. The buffering characters are used for providing the efficient writing of single arrays, characters, and strings.
Steps to create a custom exception:
- Create a new class whose name should end with Exception like ClassNameException. This is a convention to differentiate an exception class from regular ones.
- Make the class extends one of the exceptions which are subtypes of the java.lang.Exception class. Generally, a custom exception class always extends directly from the Exception class.
- Create a constructor with a String parameter which is the detail message of the exception. In this constructor, simply call the super constructor and pass the message.
Example:
// A Class that represents use-defined expception
class MyException extends Exception
{
public MyException(String s)
{
// Call constructor of parent Exception
super(s);
}
}
// A Class that uses above MyException
public class Main
{
// Driver Program
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
// Throw an object of user defined exception
throw new MyException("GeeksGeeks");
}
catch (MyException ex)
{
System.out.println("Caught");
// Print the message from MyException object
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}3. b) Difference between applet and normal java program?Create an applet with the functionalites to play, stop and repeat the audio.
Ans: Applets are small programs that are designed to execute in web browsers to generate dynamic content.
4. a) Create a swing GUI that contains a text field and a button. When the button is pressed the content in the textfield should be changed into uppercase and background color of text field should be changed.
Ans:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class UppercaseGui extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
JTextField tf;
JButton btn;
UppercaseGui(){
tf= new JTextField();
btn= new JButton("Button");
add(tf);
add(btn);
tf.setBounds(100,50,150,30);
btn.setBounds(100,100,80,30);
btn.addActionListener(this);
setLayout(null);
setSize(500,500);
setVisible(true);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
String s= tf.getText();
if (e.getSource()==btn)
{
tf.setText(s.toUpperCase());
tf.setBackground(new Color((int)(Math.random()*0x1000000)));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new UppercaseGui();
}
}Ans:Commonly used drawing methods are:
- public abstract void drawString(String str, int x, int y): is used to draw the specified string.
- public void drawRect(int x, int y, int width, int height): draws a rectangle with the specified width and height.
- public abstract void fillRect(int x, int y, int width, int height): is used to fill rectangle with the default color and specified width and height.
- public abstract void drawOval(int x, int y, int width, int height): is used to draw oval with the specified width and height.
- public abstract void fillOval(int x, int y, int width, int height): is used to fill oval with the default color and specified width and height.
- public abstract void drawLine(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2): is used to draw line between the points(x1, y1) and (x2, y2).
- public abstract boolean drawImage(Image img, int x, int y, ImageObserver observer): is used draw the specified image.
- public abstract void drawArc(int x, int y, int width, int height, int startAngle, int arcAngle): is used draw a circular or elliptical arc.
- public abstract void fillArc(int x, int y, int width, int height, int startAngle, int arcAngle): is used to fill a circular or elliptical arc.
- public abstract void setColor(Color c): is used to set the graphics current color to the specified color.
- public abstract void setFont(Font font): is used to set the graphics current font to the specified font.
import java.awt.*;
import java.applet.*;
public class DisplayImage extends Applet {
Image picture; //create
public void init() { //load
picture = getImage(getDocumentBase(),"sonoo.jpg");
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
g.drawImage(picture, 30,30, this); //display
} Ans:
| TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL (TCP) | USER DATAGRAM PROTOCOL (UDP) |
|---|---|
| TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. Connection-orientation means that the communicating devices should establish a connection before transmitting data and should close the connection after transmitting the data. | UDP is the Datagram oriented protocol. This is because there is no overhead for opening a connection, maintaining a connection, and terminating a connection. UDP is efficient for broadcast and multicast type of network transmission. |
| TCP is reliable as it guarantees delivery of data to the destination router. | The delivery of data to the destination cannot be guaranteed in UDP. |
| TCP provides extensive error checking mechanisms. It is because it provides flow control and acknowledgment of data. | UDP has only the basic error checking mechanism using checksums. |
| Sequencing of data is a feature of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). this means that packets arrive in-order at the receiver. | There is no sequencing of data in UDP. If ordering is required, it has to be managed by the application layer. |
| TCP is comparatively slower than UDP. | UDP is faster, simpler and more efficient than TCP. |
| Retransmission of lost packets is possible in TCP, but not in UDP. | There is no retransmission of lost packets in User Datagram Protocol (UDP). |
| TCP has a (20-80) bytes variable length header. | UDP has a 8 bytes fixed length header. |
| TCP is heavy-weight. | UDP is lightweight. |
| TCP doesn’t supports Broadcasting. | UDP supports Broadcasting. |
| UDP is used by DNS, DHCP, TFTP, SNMP, RIP, and VoIP. |
Java InetAddress class represents an IP address. The java.net.InetAddress class provides methods to get the IP of any host name for example www.javatpoint.com, www.google.com, www.facebook.com, etc.
5. b) What are some key classes defined in java to work with datagrams? How do you get a list of IP addresses that are assigned to a network interface?
Ans:
6. a) What is the benefit of using Prepared Statement in java? What is JDBC database connection pool? How to setup in Java?
Ans: Following are the advantages of the prepared statement:
-
By avoiding multiple compilation and execution of statements, prepared statements perform faster.
-
Using prepared statements, we can insert values to advanced datatypes such as BLOB, CLOB, OBJECT easily with the help of the setter methods provided by the PreparedStatement interface.
-
By providing setter method to set values prepared statement avoids the use of quotes and other special characters with in the query, and thereby it escapes the SQL injection attacks
Connection pooling means that connections are reused rather than created each time a connection is requested. To facilitate connection reuse, a memory cache of database connections, called a connection pool, is maintained by a connection pooling module as a layer on top of any standard JDBC driver product.
Connection pooling is a method that provides a significant improvement on performance by reusing connections rather than creating a new connection for each connection request, without requiring changes in your JDBC application code.
The steps for connection pools are−
-
Import JDBC Packages: Add import statements to your Java program to import required classes in your Java code.
-
Register JDBC Driver: This step causes the JVM to load the desired driver implementation into memory so it can fulfill your JDBC requests.
-
Database URL Formulation: This is to create a properly formatted address that points to the database to which you wish to connect.
-
Create Connection Object: Finally, code a call to the DriverManager object's getConnection( ) method to establish actual database connection.
6. b) A database "testdb" contains a table "employee" with some records having id, name, post, salary. Write a program to update the salary to 50000 whose post is "Manager".
Ans:
Inner class means one class which is a member of another class. There are basically four types of inner classes in java.
- Nested Inner class
- Method Local inner classes
- Anonymous inner classes
- Static nested classes
| Comparison Index | C++ | Java |
|---|---|---|
| Platform-independent | C++ is platform-dependent. | Java is platform-independent. |
| Mainly used for | C++ is mainly used for system programming. | Java is mainly used for application programming. It is widely used in window, web-based, enterprise and mobile applications. |
| Design Goal | C++ was designed for systems and applications programming. It was an extension of C programming language. | Java was designed and created as an interpreter for printing systems but later extended as a support network computing. It was designed with a goal of being easy to use and accessible to a broader audience. |
| Goto | C++ supports the goto statement. | Java doesn't support the goto statement. |
| Multiple inheritance | C++ supports multiple inheritance. | Java doesn't support multiple inheritance through class. It can be achieved by interfaces in java. |
| Operator Overloading | C++ supports operator overloading. | Java doesn't support operator overloading. |
| Pointers | C++ supports pointers. You can write pointer program in C++. | Java supports pointer internally. However, you can't write the pointer program in java. It means java has restricted pointer support in java. |
| Compiler and Interpreter | C++ uses compiler only. C++ is compiled and run using the compiler which converts source code into machine code so, C++ is platform dependent. | Java uses compiler and interpreter both. Java source code is converted into bytecode at compilation time. The interpreter executes this bytecode at runtime and produces output. Java is interpreted that is why it is platform independent. |
| Call by Value and Call by reference | C++ supports both call by value and call by reference. | Java supports call by value only. There is no call by reference in java. |
| Structure and Union | C++ supports structures and unions. | Java doesn't support structures and unions. |
| Thread Support | C++ doesn't have built-in support for threads. It relies on third-party libraries for thread support. | Java has built-in thread support. |
| Documentation comment | C++ doesn't support documentation comment. | Java supports documentation comment (/** ... */) to create documentation for java source code. |
| Virtual Keyword | C++ supports virtual keyword so that we can decide whether or not override a function. | Java has no virtual keyword. We can override all non-static methods by default. In other words, non-static methods are virtual by default. |
| unsigned right shift >>> | C++ doesn't support >>> operator. | Java supports unsigned right shift >>> operator that fills zero at the top for the negative numbers. For positive numbers, it works same like >> operator. |
| Inheritance Tree | C++ creates a new inheritance tree always. | Java uses a single inheritance tree always because all classes are the child of Object class in java. The object class is the root of the inheritance tree in java. |
| Hardware | C++ is nearer to hardware. | Java is not so interactive with hardware. |
| Object-oriented | C++ is an object-oriented language. However, in C language, single root hierarchy is not possible. | Java is also an object-oriented language. However, everything (except fundamental types) is an object in Java. It is a single root hierarchy as everything gets derived from java.lang.Object. |
JDBC Driver is a software component that enables java application to interact with the database. There are 4 types of JDBC drivers:
- JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
- Native-API driver (partially java driver)
- Network Protocol driver (fully java driver)
- Thin driver (fully java driver)