This document describes how an application can get access to customers data, send orders to the market and retrieve streaming quotes, order events and news.
Onboarding process for developers
Important links
Sign in to Binck API using Oauth2
Step 1: Sign in
Step 2: Retrieve authorization code
Step 3: Retrieve token
Step 4: First API request
Step 5: Refresh token
Step 7: Testing
Step 6: Production
Things to keep in mind
Get realtime data using the Binck API
Step 1: Connect to the feed
Step 2: Handle connection changes
Step 3: Start the connection
Step 4: Subscribe to data
Step 5: Extend the subscription before the token expires
Step 6: Description of the data
Step 7: Production
Things to keep in mind
If you are not interested in developing software, but want to use the API in Excel, visit the README for that example project.
Otherwise, continue reading and contact Binck with the announcement you want to develop an application using the API.
This can be done by submitting this form, where you can enter the details of the application. Important are the name of the application, the required scope (ordering, quotes, news, or only viewing) and the redirect URL. This is the URL used to redirect the user to, after signing in.
In the coming months this API will be migrated to the OpenApi of Saxobank. This means the Binck OpenApi will be obsolete. Check the new documentation for more info. There are also many samples on how to use the new API.
The API team at Binck will create a new clientId and secret with the requested privileges and sends them to you, together with a test account. The environment to test the application is sandbox. You cannot test with a real account, so orders won’t be executed on the market.
Request access to the OpenApi with this form.
Documentation of the individual endpoints can be found on developers.binck.com.
Example code and login guide can be found on Github. Great, you are here.
Releases and status updates are communicated via Twitter handle @BinckOpenApi.
Twitter can also be used for questions, or our email address openapi@binck.nl.
Some questions already have an answer in the Wiki.
The Binck API is accessible with a rest API protected with OAuth2.
“The authorization code grant is used when an application exchanges an authorization code for an access token. After the user returns to the application via the redirect URL, the application will get the authorization code from the URL and use it to request an access token. This request will be made to the token endpoint.”
More info: https://www.oauth.com/oauth2-servers/access-tokens/authorization-code-request/
Prerequisites:
- An application id with secret, realm, scope(s) and redirect URL, supplied by Binck.
Binck has a test environment, called sandbox, and a production environment. Both have an authentication provider and an API endpoint.
The authentication provider uses the OAuth2 "authorization code" flow.
For this example we use the sandbox environment, with predefined test users and passwords.
Create a 'Log in' link sending the user to:
https://login.sandbox.binck.com/am/oauth2/realms/{realm}/authorize?ui_locales={LOCALE}&client_id={CLIENT_ID}&scope={SCOPE}&state={1234zyx}&response_type={code}&redirect_uri={REDIRECT_URI}
realm – The bincknlapi realm is used for the Dutch Binck customers
ui_locales - The language to be used for the login pages, examples: fr, it, or nlBE
scope - One or more scope values (separated by space), indicating which parts of the user's account you wish to access, examples are read, write, news, quotes
state - A random string generated by your application, which you'll verify later
code - Indicates that your server expects to receive an authorization code
client_id - The client ID you received when you first created the application
redirect_uri - Indicates the URI to return the user to after authorization is complete
Don't forget to encode the URL parameters (from 'http://localhost/binck' to 'http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%2Fbinck').
The user sees the login dialog:
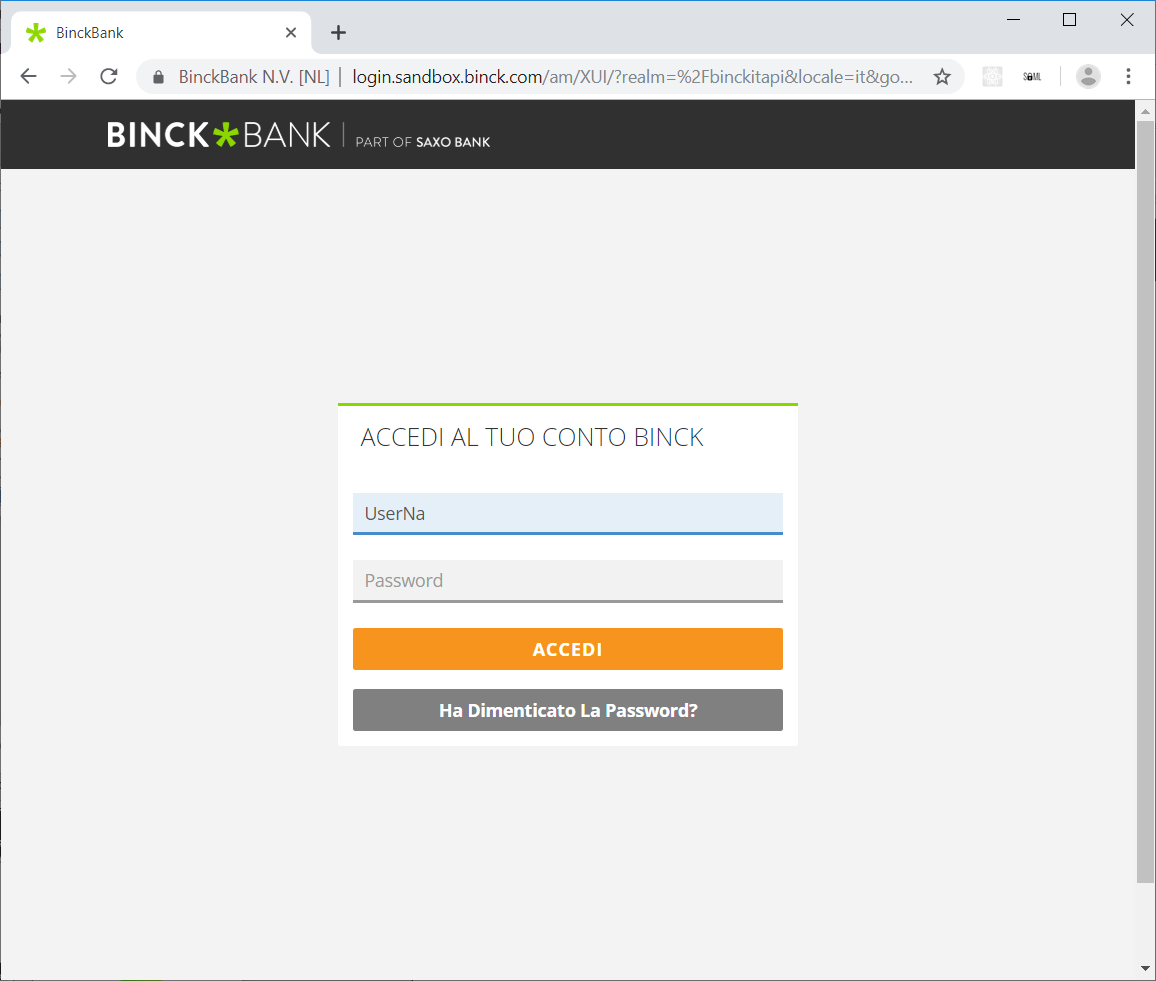
Skipping entering the validation code (SMS challenge) results in a readonly session. Placing orders won’t be allowed, even if the application requested 'write' scope.
After logging in, the user sees a dialog to give access to the thirdparty, if access is not already granted. In order to authorize, the user must login with the validation code (2FA).
If the user allows access, the service redirects the user back to your site (the redirect_uri) with an auth code in the query string.
https://{REDIRECT_URI}/?code={AUTH_CODE_HERE}&scope={SCOPE}&state={1234zyx}
code - The server returns the authorization code in the query string
state - The server returns the same state value that you passed
scope - The granted scope
You should first compare this state value to ensure it matches the one you started with. You can typically store the state value in a cookie, and compare it when the user comes back. This ensures your redirection endpoint isn't able to be tricked into attempting to exchange arbitrary authorization codes.
If the login failed, the error is returned in the query string.
https://{REDIRECT_URI}/?error_description=Resource%20Owner%20did%20not%20authorize%20the%20request&state=**1234xyz**&error=access_denied
This is an example of the error when the user denied access for your application.
With the code the application can request the token.
POST https://login.sandbox.binck.com/am/oauth2/realms/{realm}/access_token
grant_type=authorization_code
client_id=CLIENT_ID
client_secret=CLIENT_SECRET
redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI
code=AUTH_CODE_HEREThe request requires a header "Content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded".
realm - The realm to identify the customer group, for example binckitapi
grant_type - The grant type for this flow is authorization_code
client_id - The client ID you received when you first created the application
client_secret - The password of this client
redirect_uri - Must be identical to the redirect URI provided in the original link
code - This is the code you received in the query string
Because this request contains your secret, it cannot be done in javascript, or any other client side application.
The response will contain:
{
"access_token": "5af56faa-8cd9-466b-81b1-5f2eadafca1f",
"refresh_token": "dcdd4c1e-4241-405f-ae1c-2dc14e31d895",
"scope": "read write quotes news",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 3599
}access_token – The token to be used when calling the API
expires_in - The time in seconds the token will be valid
refresh_token – The token used to request a new access_token, just before token expiry
scope – The requested scope, for example “read write”
token_type – You retrieved a Bearer token
The expiry time is one hour. However, if there are no requests in 30 minutes, the session will expire as well (idle time = 30 minutes).
If there is a problem receiving the code, an error will be returned. If there is no problem with the connection, the auth server responds with an error object in this format:
{
"error_description": "Client authentication failed",
"error": "invalid_client"
}The token grants access to the API. For example, to get the accounts of the user.
Before proceeding, the API connection can be tested without token, by using the version endpoint.
https://api.sandbox.binck.com/api/v1/version
This GET request returns, if directly requested, a json response with the build date and version of the API.
GET https://api.sandbox.binck.com/api/v1/version{
"Accept": "application/json; charset=utf-8",
"Authorization": "Bearer " + ACCESS_TOKEN
}access_token - The token retrieved in step 3
Endpoint:
https://api.sandbox.binck.com/api/v1/accounts
The request is granted access if the token is supplied.
The complete API description can be found at https://developers.binck.com.
The errors are returned in a uniform layout.
{
"developerMessage": "Unauthorized",
"endUserMessage": "Non sei autorizzato.",
"errorCode": "Unauthorized",
"errorId": "unknown"
}developerMessage – A notification for the developer of the app. Not meant to be shown to end users
endUserMessage – A translated error, in the language of the end user, to show to the end user
errorCode – A code, which can be used for development
errorId – If applicable, an error id to report back to Binck, for trouble shooting
The token request contains an expiration time. After this time, the token is no longer valid.
So, before the token expires, a new token must be requested. For this, we have a refresh token.
POST https://login.sandbox.binck.com/am/oauth2/realms/{realm}/access_token
grant_type=refresh_token
client_id=CLIENT_ID
client_secret=CLIENT_SECRET
refresh_token=REFRESH_TOKEN_HERErealm - The realm to identify the customer group, for example binckitapi
grant_type - The grant type to refresh a token is refresh_token
client_id - The client ID you received when you first created the application
client_secret - The password of this client
refresh_token – The token received when requesting the initial token
As with the initial token retrieval, this request is not allowed from any client application hosted on the customers machine.
The response is the same as the initial token request. See step 3.
For realtime streams, see documentation on realtime refresh on how to inject the new token to that connection.
The sandbox functionality can be compared with the website. The website with the same data as sandbox can be accessed using these URLs:
- Binck BE: https://web.sandbox.binck.be/logon/
- Binck IT: https://web.sandbox.binck.it/logon/
- Binck NL: https://web.sandbox.binck.nl/logon/
The production environment is the same as sandbox, but, with real customers and live data.
The application is can go to production when development is finished and the application is thouroughly tested on sandbox. This is only for individual usage.
When the application is used by more accounts than yours, Binck requires a thirdparty agreement.
Use these URL’s:
https://login.binck.com/am/oauth2/
https://api.binck.com/api/v1/
If there is a release and there is a need to set the Binck backend in maintenance, this error message is returned for every request:
{
"DeveloperMessage": "Temporary maintenance mode",
"EndUserMessage": "BinckBank is currently down for planned maintenance. We expect to be back in a couple of hours. Thanks for your patience.",
"ErrorCode": "ServiceUnavailable",
"ErrorId": 503
}Your application must be able to handle this error message.
The description of the available endpoints is located here: https://developers.binck.com, and an example of a client written in javascript can be found here: https://github.com/binckbank-api/client-js/.
- Never ever leak the secret. Don’t put in in frontend code.
- The secret will change periodically, keep it in a controlled environment.
- The customer login is on person level. This means if a customer has more than one account, the customer might need to select the account to use for the application. There are multiple account types, not all account types have trading options (example is the savings account).
- Request small portions of data, using paging. If you must display 10 transactions, request ten transactions.
- When placing an order, comply with the rules and regulations. Show the KID document if available, give an option to display the order costs.
- Be prepared for error messages. Never display the developer message, but your own one. Developer messages are for logging and trouble shooting.
- End user messages must be shown, they are in the locale language of the customer.
- When the systems of Binck are down, the error message is stating this. Sign in page shows a maintenance page.
- When requesting the login page, supply the locale of the customer. If not, the fallback might not be the desired language of the country.
- Instrument IDs might change overnight. When caching, keep this in mind.
- The instrument IDs on sandbox differ from the ones on production.
- The API has a limit of 50 requests per minute. If exceeded, the customer might be logged out, resulting in an UnAuthorized response.
- The token can be refreshed for 24 hours. After this, the customer must login again.
- We respect a REST convention that trailing slashes are not allowed, so
https://api.sandbox.binck.com/api/v1/accountsis the correct notation. - Orders on sandbox won't go to the market. If you need a (partial) execution, send us an email with the details of the order you want to be executed.
This document describes the realtime feed available for customers.
The library used to push data is SignalR:
ASP.NET Core SignalR is an open-source library that simplifies adding real-time web functionality to apps. Real-time web functionality enables server-side code to push content to clients instantly.
Communication is done using WebSockets, Server-Sent Events, or Long Polling. SignalR automatically chooses the best transport method that is within the capabilities of the server and client.
More info: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/signalr.
For SignalR are client libraries available in Java, Javascript and .NET Core. In this example Javascript is used, with the NPM package here: https://www.npmjs.com/package/@microsoft/signalr.
Prerequisites:
- A token retrieved using the OAuth2 Authentication flow, as described in the chapter Logon to Binck API using Oauth2.
Scope:
- quotes (for instrument prices)
- news (for news)
- read and/or write (for order updates)
Binck has a test environment (sandbox) and a production environment. Both have the realtime feed.
For this example we use the sandbox environment, with predefined test users and passwords.
The instruction for creating the client can be found here: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/signalr/javascript-client.
The API allows only one session per token. All subsequent connections will be refused.
The following code creates and starts a connection:
var options = {
accessTokenFactory: function () {
var accessToken = "{TOKEN_RETRIEVED_FROM_LOGIN.BINCK.COM}";
console.log("AccessToken used in streamer request: " + accessToken);
return accessToken;
}
};
connection = new signalR.HubConnectionBuilder()
.withUrl("https://realtime.sandbox.binck.com/stream/v1", options)
.configureLogging(signalR.LogLevel.Information) // Might be 'Trace' for testing
.build();accessToken – The Bearer token
url - The URL of the realtime channel
The user might stop the connection. Or something can go wrong with the server. Then the application might do a reconnect, or just show this to the user.
The following code configures the event:
connection.onclose(function () {
console.log("The connection has been closed.");
alert("disconnected");
});The following code starts the connection:
connection.start()
.then(function () {
console.log("The streamer has been started.");
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.error(error);
});That’s it. The application is now ready to subscribe to messages.
News can differ per account. For example, asset management accounts see different messages than trading accounts.
In general, news is English, or in the locale of the customer.
Required scope: “news”.
Configure the callback using this code:
connection.on("News", function (data) {
console.log(data);
});Create the subscription for the account using this code:
connection.invoke("SubscribeNews", accountNumber)
.then(function (subscriptionResponse) {
if (subscriptionResponse.isSucceeded) {
console.log("Subscribed to news.");
} else {
console.log("Error. Is accountNumber valid for this session?");
}
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.error(error);
});Stop listening to the news broadcast can be achieved by invoking UnSubscribeNews (no account number).
Quotes are not always realtime. This differs based on the subscription of the customer for realtime feeds on certain markets. If there is no realtime subscription, quotes are delayed, but still streaming. There is a limit on the number of quotes to subscribe, of 3.000. And to the number of instruments to be added to the subscription. Blocks per subscription update must be at most 100.
Required scope: “quotes”.
Configure the callback using this code:
connection.on("Quote", function (data) {
console.log(data);
});Create the subscription for the account using this code:
connection.invoke(
"SubscribeQuotes",
accountNumber,
instrumentIds, // Array of instrumentsIds
quoteSubscriptionLevel
)
.then(function (subscriptionResponse) {
if (subscriptionResponse.isSucceeded) {
console.log("Succeeded, instrument #: " + subscriptionResponse.subcount);
} else {
console.log("Error. Is accountNumber valid for this session?");
}
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.error(error);
});The instrumentIds must be an array of instrumentIds.
SubscriptionLevel is one of these values:
var QuoteSubscriptionLevel = {
// Retrieve only the last, high, low, cumulative volume and open prices.
TRADES: "Trades",
// In addition to trades, retrieve the bid1 and ask1 of the book.
TOPOFBOOK: "TopOfBook",
// In addition to trades, retrieve the full book, if available.
BOOK: "Book"
};In the response the number of subscriptions is returned. Use this to validate if there are not to many instruments in the subscription. This might make the connection slow.
Stop listening to the quote broadcast can be achieved by invoking UnSubscribeQuotes (no account number).
connection.invoke(
"UnSubscribeQuotes",
instrumentIds // Array of instrumentsIds
)
.then(function (subscriptionResponse) {
if (subscriptionResponse.isSucceeded) {
console.log("Unsubscribe succeeded, instrument #: " + subscriptionResponse.subcount);
} else {
// Internal issue - should never occur
console.log("Quote unsubscribe failed");
}
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.error(error);
});The order execution events are published when there is a change in portfolio positions.
Required scope: “read” or “write”.
Configure the callback using this code:
connection.on("OrderExecution", function (data) {
console.log(data);
});Subscribing to order events, modifications and executions is combined, using this code:
connection.invoke("SubscribeOrders", accountNumber)
.then(function (subscriptionResponse) {
if (subscriptionResponse.isSucceeded) {
console.log("Subscribed to order events.");
} else {
console.log("Error. Is accountNumber valid for this session?");
}
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.error(error);
});Stop listening to the order broadcast can be achieved by invoking UnSubscribeOrders (no account number).
The order modification events are send when the pending order is modified by the customer.
Required scope: “read” or “write”.
Configure the callback using this code:
connection.on("OrderStatus", function (data) {
console.log(data);
});The order change events are send when the order is placed, (partially) executed, or cancelled, etc. These updates are not as detailed as in the orders endpoint, so requesting the order data from the API might be necessary.
Required scope: “read” or “write”.
Configure the callback using this code:
connection.on("OrderModified", function (data) {
console.log(data);
});The realtime feed will stop after the token has been expired. When the application has refreshed the token, there is a need to extend the subscription.
See the documentation of the OAuth2 flow on how to handle a token refresh.
Extend the subscription using this code:
connection.invoke("ExtendSubscriptions", "{NEW_TOKEN_RETRIEVED_FROM_LOGIN.BINCK.COM}")
.then(function () {
console.log("Session extended.");
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.error(error);
});A news object is structured as following:
{
"cul": "nl-BE", // Culture of the news message
"dt": "2019-04-23T18:25:43.511Z", // Publishing datetime
"head": "Title", // Subject, unformatted
"body": "Body", // News body (optional)
"fmt": "html", // Format of the body
"iids": ["instrumentId"] // Array of instrument ids
}cul (culture) The messages can be in different cultures, depending on the news subscription of the customer.
dt The datetime the message was published, in UTC format.
head The subject of the message. If prefixed with an *, probably it is only a header. This is the journalist working on a news message, sending the headlines in front.
The * is just a standard. If the message is only a headline, there is no body property.
body Optional news message. Can come in HTML format or plain text, depending on the news supplier.
fmt (format) Format of the body. Can be ‘html’ or ‘plain’.
iids (instrument ids) If the message is applicable for one or more tradable instruments, this array contains the instrument ids.
An order object is structured as following:
{
"accountNumber": "accountNumber", // Account
"number": orderNumber, // Together with account, this identifies the order
"referenceId": "external reference" // This can be your reference, provided with an order
"instrument": {
"id": "instrumentId" // Instrument id
},
"status": "placed", // New order status, like “placed”, or “canceled”
"limitPrice": 5, // New limit price, if applicable
"type": "orderType", // Order type, like “limit”
"expirationDate": "2019-01-16T00:00:00Z", // Date when order expires
"dt": "2019-01-16T10:21:28Z" // Date when order was placed
}The status can be one of the following:
- placed: It is a new order
- canceled: Order has been canceled
- expired: Order is expired
- completelyExecuted: Order is completely executed
- partiallyExecuted: Applicable when order is executed in multiple parts
- remainderExecuted: Applicable when order is executed in multiple parts
A quote object is structured with an array of quote objects, as following:
{
"id": "instrumentId", // Instrument id
"lvl": 0, // Subscription level of customer
"sdt": "2019-04-23T18:25:43.511Z", // Time of sending packet
"qt": [{
"msg": "qu", // Quote Init, or Quote Update
"typ": "lst", // Last, High, Low, Close, Open, etc.
"prc": 7.78, // New price
"vol": 100, // Volume
"ord": 3, // Order size (book)
"dt": "2019-04-23T18:25:43.511Z", // Generation datetime
"tags": "C" // Optional flag for (C)ancel, (M)arket, etc.
}]
}msg (message) This property is used to differentiate between object formats.
- qi: An initial quote, used to populate the page. By populating from SDI, a possible gap in the quotes is prevented. Highlighting is not needed.
- qu: A quote update. Highlighting can be done.
The initial quote is send to prevent empty quotes and possible gaps. But, an update might arrive before the initial quote. If this is the case, ignore the initial quote.
typ (type) The type of quote, where to differentiate the following types:
- lst: Last price
- vol: Cumulative volume of the day
- cls: Close price
- opn: Opening price
- hgh: Highest price of the day
- low: Lowest price of the day
- bid: The bid price
- ask: Ask price
- thp: Theoretical price
- ivl: Implied volatility
- idv: Implied div
- iir: Implied IR
- set: Settlement price
- oir: Open interest rate
id (identification) The hashed instrument id.
prc (price) This property has the price of the instrument. Zero for cumulative volumes.
vol (volume) This property contains the amount of traded instruments. Zero for non-tradeable instruments like indices, and zero for close, open, high and low prices.
dt (datetime) This property contains the date and time of the price, in local time of the market.
tags A quote might be taged with one of the following tags:
- C (cancel): A new cycle will start. The quotes for the instrument must be removed.
- M (market): Show the maket indicator in the bid and ask cells.
- O (open): Show an open indicator.
- X (exclude): Exclude this quote from intraday charts, but show in overview lists.
The production environment is the same as sandbox, only with real customers and live data.
Use this URL: https://realtime.binck.com/stream/v1/
Example code (in JavaScript) can be found on GitHub: https://github.com/binckbank-api/client-js.
- Testing the connection can be done using the version endpoint: https://realtime.sandbox.binck.com/version.
- Binck allows one active connection per token. The second connection will be disconnected when subscribing for updates.