Name
双范围过滤趋势跟踪策略Dual-Range-Filter-Trend-Tracking-Strategy
Author
ChaoZhang
Strategy Description
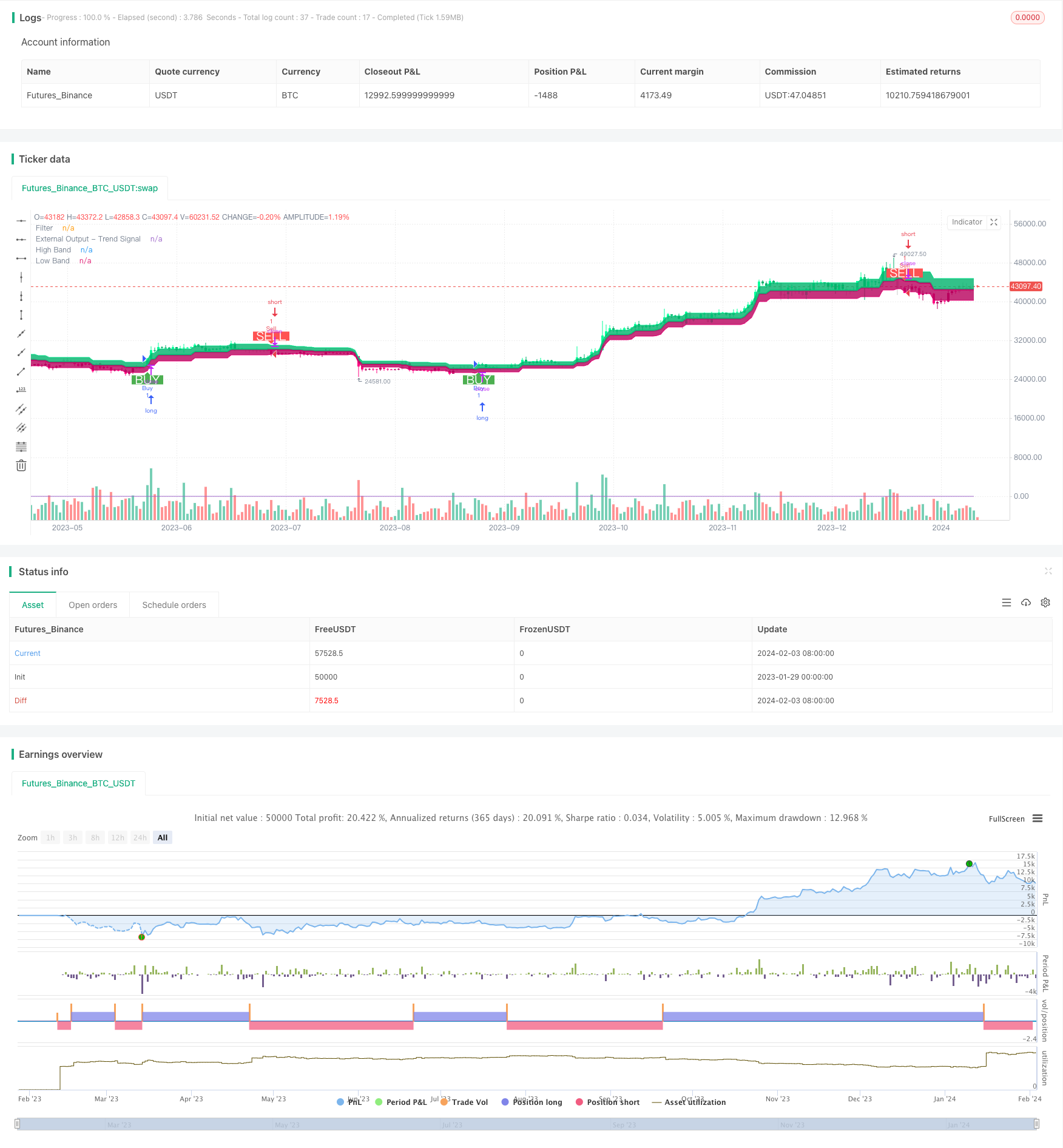
双范围过滤趋势跟踪策略(Dual Range Filter Trend Tracking Strategy)是一个利用双EMA范围过滤来识别趋势方向,并跟踪趋势的量化交易策略。该策略结合双均线过滤和ATR范围计算,可以有效识别中长线趋势的方向,并利用追踪止损来锁定利润。
该策略的核心是双EMA范围过滤。它计算K线的ATR范围并平滑,然后结合两个EMA来定位K线在范围内的位置,判断目前是否处在趋势之中。当价格突破范围时,就表明趋势发生转变。
具体来说,策略首先计算K线的ATR范围大小,然后结合两个EMA对其进行平滑。ATR范围代表了K线的正常波动区间。当价格超出这个区间时,就意味着趋势发生变化。策略会记录价格突破EMA范围的方向。当方向发生变化时,说明趋势转折,这时可以选择进入场内。
在进场后,策略利用浮动止损来锁定利润。在持仓期间,它会实时判断K线是否回落超出范围之外,如果发生回落就会退出当前头寸。这可以有效锁定趋势交易的利润。
双范围过滤趋势跟踪策略结合了均线过滤和范围计算的优势,可以准确判断趋势的方向,避免在震荡行情中频繁进出场。具体优势如下:
- 利用ATR原理判断K线波动范围,避免在震荡市场无方向进入场内
- 双EMA过滤提高判断准确性,降低假信号
- 实时浮动止损,可以有效锁定趋势利润
- 策略逻辑简单清晰,容易理解和优化
该策略也存在一些风险,主要集中在以下几个方面:
- 大幅度跳空可以击穿ATR范围,导致提前入场
- 强势趋势行情中,止损可能过早被触发
- 参数设置不当也会影响策略表现
对于这些风险,可以通过适当优化参数、防止假突破、判断趋势强度等方法来解决。
双范围过滤趋势跟踪策略还具备进一步优化的潜力,主要的优化方向包括:
- 优化ATR参数,平滑K线波动范围
- 结合交易量指标避免假突破
- 判断趋势强度,区分单次突破和可持续趋势
- 优化止损点位,在保证利润的前提下追踪长趋势
通过这些优化,可以使策略在更多市场环境下获得稳定收益。
双范围过滤趋势跟踪策略整合了均线过滤和ATR范围判断的多种优点,可以有效识别中长线可持续趋势的方向和入场时机。它只在趋势发生变化时进入场内,并利用浮动止损来锁定利润。该策略逻辑简洁清晰,非常适合中长线趋势交易。通过持续优化参数和判断规则,该策略可以在多种市场中获得较好收益。
||
The Dual Range Filter Trend Tracking Strategy is a quantitative trading strategy that utilizes dual EMA range filtering to identify trend direction and track trends. This strategy combines dual moving average filtering and ATR range calculation to effectively recognize mid-to-long term trend direction and lock in profits with trailing stop loss.
The core of this strategy is the dual EMA range filtering. It calculates the ATR range of candlesticks and smoothes it, then uses two EMAs to locate the position of candlesticks within the range to determine if it is currently in a trend. When the price breaks through the range, it signals a change in the trend.
Specifically, the strategy first calculates the ATR range size of the candlesticks, and then smoothes it with two EMAs. The ATR range represents the normal fluctuation range of the candlesticks. When the price exceeds this range, it means a change in the trend has occurred. The strategy records the direction when the price breaks through the EMA range. When the direction changes, it means a trend reversal has occurred, and that is when it can choose to enter the market.
After entering the market, the strategy uses a floating stop loss to lock in profits. During the holding period, it constantly judges whether the candlestick has fallen back out of range. If a pullback occurs, it will exit the current position. This can effectively lock the profits from trend trading.
The Dual Range Filter Trend Tracking Strategy combines the advantages of moving average filtering and range calculation to accurately determine trend direction and avoids frequently entering and exiting the market in ranging markets. The specific advantages are:
- Use ATR principle to judge candlestick fluctuation range, avoids entering the market without direction during ranging market
- The dual EMA filter improves judgment accuracy and reduces false signals
- Real-time floating stop loss can effectively lock in trend profits
- Simple and clear strategy logic, easy to understand and optimize
There are also some risks with this strategy, mainly in the following aspects:
- Large gaps can break through the ATR range, resulting in premature entry
- In strong trending markets, the stop loss may be triggered prematurely
- Improper parameter settings also affects strategy performance
To address these risks, methods such as optimizing parameters appropriately, preventing false breakouts, judging trend strength can be used to solve them.
The Dual Range Filter Trend Tracking Strategy also has potential for further optimization, with the main optimization directions including:
- Optimize ATR parameters to smooth candlestick fluctuation range
- Incorporate volume indicators to avoid false breakouts
- Judge trend strength to distinguish one-time breakouts and sustainable trends
- Optimize stop loss price to track long trends while ensuring profit
Through these optimizations, the strategy can achieve steady profits in more market environments.
The Dual Range Filter Trend Tracking Strategy integrates the various advantages of moving average filtering and ATR range judgment, and can effectively identify the direction and entry timing of sustainable mid-to-long term trends. It only enters the market when trends change, and uses a floating stop loss to lock in profits. This strategy has simple and clear logic and is very suitable for mid-to-long term trend trading. Through continuous optimization of parameters and judgment rules, this strategy can achieve good returns across various markets.
[/trans]
Strategy Arguments
| Argument | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| v_input_1 | 0 | Filter Type: Type 1 |
| v_input_2 | 0 | Movement Source: Close |
| v_input_3 | 2.618 | Range Size |
| v_input_4 | 0 | Range Scale: Average Change |
| v_input_5 | 14 | Range Period (for ATR, Average Change, and Standard Deviation) |
| v_input_6 | true | Smooth Range |
| v_input_7 | 27 | Smoothing Period |
| v_input_8 | true | Average Filter Changes |
| v_input_9 | 2 | Number Of Changes To Average |
| v_input_10 | 100 | Take Profit Percentage |
| v_input_11 | 100 | Stop Loss Percentage |
Source (PineScript)
/*backtest
start: 2023-01-29 00:00:00
end: 2024-02-04 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
strategy("Range Filter [DW] & Labels", shorttitle="RF [DW] & Labels", overlay=true)
//Conditional Sampling EMA Function
Cond_EMA(x, cond, n)=>
var val = array.new_float(0)
var ema_val = array.new_float(1)
if cond
array.push(val, x)
if array.size(val) > 1
array.remove(val, 0)
if na(array.get(ema_val, 0))
array.fill(ema_val, array.get(val, 0))
array.set(ema_val, 0, (array.get(val, 0) - array.get(ema_val, 0))*(2/(n + 1)) + array.get(ema_val, 0))
EMA = array.get(ema_val, 0)
EMA
//Conditional Sampling SMA Function
Cond_SMA(x, cond, n)=>
var vals = array.new_float(0)
if cond
array.push(vals, x)
if array.size(vals) > n
array.remove(vals, 0)
SMA = array.avg(vals)
SMA
//Standard Deviation Function
Stdev(x, n)=>
sqrt(Cond_SMA(pow(x, 2), 1, n) - pow(Cond_SMA(x, 1, n), 2))
//Range Size Function
rng_size(x, scale, qty, n)=>
ATR = Cond_EMA(tr(true), 1, n)
AC = Cond_EMA(abs(x - x[1]), 1, n)
SD = Stdev(x, n)
rng_size = scale=="Pips" ? qty*0.0001 : scale=="Points" ? qty*syminfo.pointvalue : scale=="% of Price" ? close*qty/100 : scale=="ATR" ? qty*ATR :
scale=="Average Change" ? qty*AC : scale=="Standard Deviation" ? qty*SD : scale=="Ticks" ? qty*syminfo.mintick : qty
//Two Type Range Filter Function
rng_filt(h, l, rng_, n, type, smooth, sn, av_rf, av_n)=>
rng_smooth = Cond_EMA(rng_, 1, sn)
r = smooth ? rng_smooth : rng_
var rfilt = array.new_float(2, (h + l)/2)
array.set(rfilt, 1, array.get(rfilt, 0))
if type=="Type 1"
if h - r > array.get(rfilt, 1)
array.set(rfilt, 0, h - r)
if l + r < array.get(rfilt, 1)
array.set(rfilt, 0, l + r)
if type=="Type 2"
if h >= array.get(rfilt, 1) + r
array.set(rfilt, 0, array.get(rfilt, 1) + floor(abs(h - array.get(rfilt, 1))/r)*r)
if l <= array.get(rfilt, 1) - r
array.set(rfilt, 0, array.get(rfilt, 1) - floor(abs(l - array.get(rfilt, 1))/r)*r)
rng_filt1 = array.get(rfilt, 0)
hi_band1 = rng_filt1 + r
lo_band1 = rng_filt1 - r
rng_filt2 = Cond_EMA(rng_filt1, rng_filt1 != rng_filt1[1], av_n)
hi_band2 = Cond_EMA(hi_band1, rng_filt1 != rng_filt1[1], av_n)
lo_band2 = Cond_EMA(lo_band1, rng_filt1 != rng_filt1[1], av_n)
rng_filt = av_rf ? rng_filt2 : rng_filt1
hi_band = av_rf ? hi_band2 : hi_band1
lo_band = av_rf ? lo_band2 : lo_band1
[hi_band, lo_band, rng_filt]
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Inputs
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Filter Type
f_type = input(defval="Type 1", options=["Type 1", "Type 2"], title="Filter Type")
//Movement Source
mov_src = input(defval="Close", options=["Wicks", "Close"], title="Movement Source")
//Range Size Inputs
rng_qty = input(defval=2.618, minval=0.0000001, title="Range Size")
rng_scale = input(defval="Average Change", options=["Points", "Pips", "Ticks", "% of Price", "ATR", "Average Change", "Standard Deviation", "Absolute"], title="Range Scale")
//Range Period
rng_per = input(defval=14, minval=1, title="Range Period (for ATR, Average Change, and Standard Deviation)")
//Range Smoothing Inputs
smooth_range = input(defval=true, title="Smooth Range")
smooth_per = input(defval=27, minval=1, title="Smoothing Period")
//Filter Value Averaging Inputs
av_vals = input(defval=true, title="Average Filter Changes")
av_samples = input(defval=2, minval=1, title="Number Of Changes To Average")
// New inputs for take profit and stop loss
take_profit_percent = input(defval=100.0, minval=0.1, maxval=1000.0, title="Take Profit Percentage", step=0.1)
stop_loss_percent = input(defval=100, minval=0.1, maxval=1000.0, title="Stop Loss Percentage", step=0.1)
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Definitions
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//High And Low Values
h_val = mov_src=="Wicks" ? high : close
l_val = mov_src=="Wicks" ? low : close
//Range Filter Values
[h_band, l_band, filt] = rng_filt(h_val, l_val, rng_size((h_val + l_val)/2, rng_scale, rng_qty, rng_per), rng_per, f_type, smooth_range, smooth_per, av_vals, av_samples)
//Direction Conditions
var fdir = 0.0
fdir := filt > filt[1] ? 1 : filt < filt[1] ? -1 : fdir
upward = fdir==1 ? 1 : 0
downward = fdir==-1 ? 1 : 0
//Colors
filt_color = upward ? #05ff9b : downward ? #ff0583 : #cccccc
bar_color = upward and (close > filt) ? (close > close[1] ? #05ff9b : #00b36b) :
downward and (close < filt) ? (close < close[1] ? #ff0583 : #b8005d) : #cccccc
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Outputs
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Filter Plot
filt_plot = plot(filt, color=filt_color, transp=0, linewidth=3, title="Filter")
//Band Plots
h_band_plot = plot(h_band, color=#05ff9b, transp=100, title="High Band")
l_band_plot = plot(l_band, color=#ff0583, transp=100, title="Low Band")
//Band Fills
fill(h_band_plot, filt_plot, color=#00b36b, transp=85, title="High Band Fill")
fill(l_band_plot, filt_plot, color=#b8005d, transp=85, title="Low Band Fill")
//Bar Color
barcolor(bar_color)
//External Trend Output
plot(fdir, transp=100, editable=false, display=display.none, title="External Output - Trend Signal")
// Trading Conditions Logic
longCond = close > filt and close > close[1] and upward > 0 or close > filt and close < close[1] and upward > 0
shortCond = close < filt and close < close[1] and downward > 0 or close < filt and close > close[1] and downward > 0
CondIni = 0
CondIni := longCond ? 1 : shortCond ? -1 : CondIni[1]
longCondition = longCond and CondIni[1] == -1
shortCondition = shortCond and CondIni[1] == 1
// Strategy Entry and Exit
strategy.entry("Buy", strategy.long, when = longCondition)
strategy.entry("Sell", strategy.short, when = shortCondition)
// New: Close conditions based on percentage change
long_take_profit_condition = close > strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + take_profit_percent / 100)
short_take_profit_condition = close < strategy.position_avg_price * (1 - take_profit_percent / 100)
long_stop_loss_condition = close < strategy.position_avg_price * (1 - stop_loss_percent / 100)
short_stop_loss_condition = close > strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + stop_loss_percent / 100)
strategy.close("Buy", when = shortCondition or long_take_profit_condition or long_stop_loss_condition)
strategy.close("Sell", when = longCondition or short_take_profit_condition or short_stop_loss_condition)
// Plot Buy and Sell Labels
plotshape(longCondition, title = "Buy Signal", text ="BUY", textcolor = color.white, style=shape.labelup, size = size.normal, location=location.belowbar, color = color.green, transp = 0)
plotshape(shortCondition, title = "Sell Signal", text ="SELL", textcolor = color.white, style=shape.labeldown, size = size.normal, location=location.abovebar, color = color.red, transp = 0)
// Alerts
alertcondition(longCondition, title="Buy Alert", message = "BUY")
alertcondition(shortCondition, title="Sell Alert", message = "SELL")
Detail
https://www.fmz.com/strategy/441059
Last Modified
2024-02-05 11:15:28