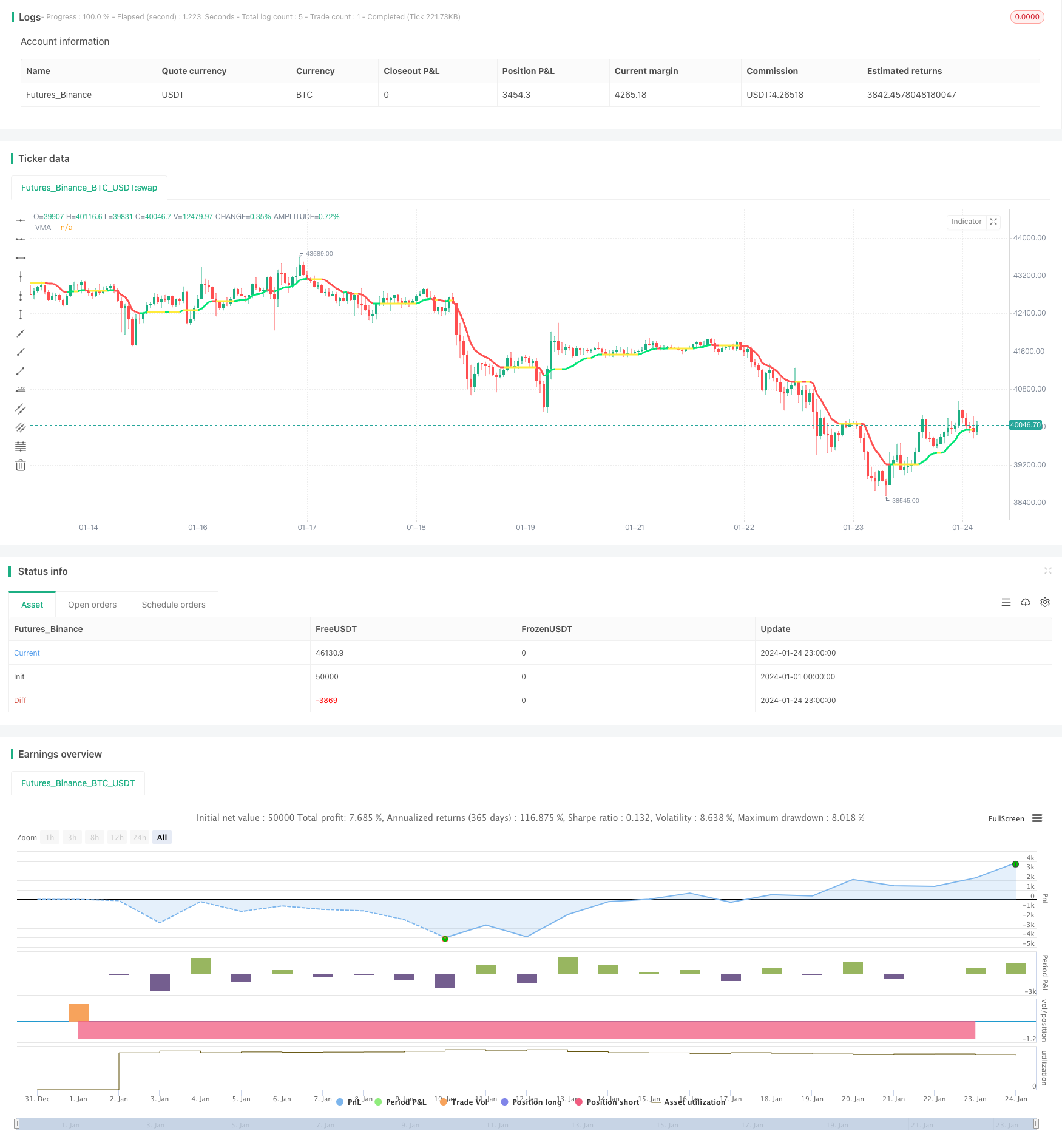
Name
可变移动平均线-TradingVMA-策略TradingVMA-Variable-Moving-Average-Trading-Strategy
Author
ChaoZhang
Strategy Description
TradingVMA策略是一个基于可变移动平均线的量化交易策略。该策略运用变化的移动平均线来捕捉市场趋势,并据此产生交易信号。
TradingVMA策略的核心是计算可变长度的移动平均线(Variable Moving Average,VMA)。移动平均线是一种广为人知的技术指标,它计算一定周期内的平均价格。TradingVMA策略所使用的VMA具有变化的周期长度。
具体来说,该策略首先计算一系列中间量,如价格方向运动指标(PDM,MDIM)、平滑处理后的数据(PDMs,MDMs)。这些数据最终被用来得到指标强度(iS)。该指标反映了价格波动的力度。
然后,TradingVMA策略根据指标强度,动态调整移动平均线的长度。当市场波动加大时,移动平均线的周期会变短,反之周期会加长。这样可以更快地响应市场变化。
最后,策略比较当前价格与VMA的大小,产生交易信号。价格高于VMA时做多,价格低于VMA时做空。
TradingVMA策略具有以下主要优势:
-
可变周期 Filters Noise 更稳定 - 可变移动平均线周期随市场变化调整,可以滤波噪音,获取更稳定的趋势信号。
-
快速响应价格变化 Improves Responsiveness - 可变移动平均线可以快速响应价格变化,捕捉新趋势的转折点。
-
减少交易频率 Reduce Overtrading - 相比固定周期指标,TradingVMA可以减少不必要的交易次数。
-
可自定义参数 Flexible Parameters - 该策略允许用户根据自己的偏好选择参数,适应不同市场环境。
TradingVMA策略也存在以下主要风险:
-
可错过快速反转 Miss Rapid Reversals - 当趋势快速反转时,持续调整的移动平均线可能会延迟做出反应。
-
受跟随偏差影响 Lagging Bias - 所有移动平均线策略或多或空都会有一定程度的跟随偏差。
-
多空号错误 Wrong Signals - 在横盘整理的市场中,TradingVMA可能会产生错误的多空信号。
-
参数优化难度 Parameter Optimization Difficulty - 找到最佳参数组合可能会比较困难。
可以通过止损,调整参数组合等方式来控制这些风险。
TradingVMA策略还可以从以下几个方向进行优化:
-
整合其他指标 Combine Other Indicators - 与其它趋势、趋势反转等指标组合使用可以提高信号质量。
-
最优参数寻优 Parameter Optimization - 通过历史回测和参数优化找到最佳参数组合。
-
自适应交易规则 Adaptive Trading Rules - 根据不同市场环境采取不同的开仓规则、止损规则等。
-
算法交易系统化 Systemization - 将策略算法化和系统化,便于回测优化。
TradingVMA是一种自适应的量化策略。它使用特殊设计的VMA指标来捕捉市场趋势,具有响应迅速、过滤噪音的优势。该策略可以通过多种方式进行优化,以获得更好的表现。但也不能完全避免跟随偏差等问题的存在。总体来说,TradingVMA是一个非常有前景的趋势跟随策略。
||
The TradingVMA strategy is a quantitative trading strategy based on variable moving average lines. It utilizes changing moving averages to capture market trends and generate trading signals accordingly.
The core of the TradingVMA strategy is the calculation of variable length moving averages (Variable Moving Average, VMA). The moving average is a widely known technical indicator that computes the average price over a certain period. The VMA used in the TradingVMA strategy has varying period lengths.
Specifically, the strategy first computes a series of intermediate quantities, such as Price Directional Movement Indicator (PDM, MDIM), smoothed data (PDMs, MDMs). These data are eventually used to obtain the indicator strength (iS). This indicator reflects the intensity of price fluctuations.
Then, the TradingVMA strategy dynamically adjusts the moving average period based on the indicator strength. When market volatility increases, the moving average period becomes shorter, and vice versa. This allows faster response to market changes.
Finally, the strategy compares the current price with the VMA to generate trading signals. It goes long when price is above VMA and goes short when price is below VMA.
The TradingVMA strategy has the following main advantages:
-
Variable Period Filters Noise More Steady – The variable moving average period adapts to market changes for filtering out noise and more stable trend signals.
-
Faster Response to Price Changes Improves Responsiveness – The variable moving average can respond swiftly to price changes and capture trend reversal points.
-
Reduces Trading Frequency Less Overtrading - Compared to fixed-period indicators, TradingVMA can reduce unnecessary trades.
-
Customizable Parameters Flexibility - The strategy allows users to select parameters based on their preferences to suit different market environments.
The TradingVMA strategy also has the following primary risks:
-
Missing Rapid Reversals – When trends reverse rapidly, the continuously adjusting moving average may lag in responding.
-
Lagging Bias – All moving average strategies have some degree of lagging bias, either long or short.
-
Wrong Signals –TradingVMA may generate incorrect long/short signals in range-bound sideways markets.
-
Difficult Parameter Optimization – Finding the optimal parameter combination can be challenging.
These risks can be controlled via methods like stop losses, adjusting parameter combinations, etc.
The TradingVMA strategy can also be enhanced in the following aspects:
-
Combine Other Indicators – Using with other trend, counter-trend indicators can improve signal quality.
-
Parameter Optimization – Discover optimum parameters via backtesting and optimization.
-
Adaptive Trading Rules – Employ different entry rules, stop losses per market regime.
-
Systemization – Algorithmize and systemize the strategy for easier optimization.
TradingVMA is an adaptive quantitative strategy. It captures market trends using a specially designed VMA indicator, with the edge of being responsive and filtering out noise. The strategy can be upgraded in multiple ways for better performance. But some inherent issues like lagging bias may persist. Overall, TradingVMA is a promising trend-following strategy.
[/trans]
Strategy Arguments
| Argument | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| v_input_1 | 5 | VMA Length |
| v_input_2 | true | Show Trend Direction Colors |
| v_input_3 | false | Use take profit? |
| v_input_4 | 100 | Take profit pips |
| v_input_5 | false | Use stop loss? |
| v_input_6 | 100 | Stop loss pips |
| v_input_7 | true | From Day |
| v_input_8 | true | From Month |
| v_input_9 | 2000 | From Year |
| v_input_10 | 31 | To Day |
| v_input_11 | 12 | To Month |
| v_input_12 | 2019 | To Year |
Source (PineScript)
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-01 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-24 23:59:59
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © laptevmaxim92
//@version=4
strategy("Variable Moving Average Strategy", overlay=true)
src=close
l =input(5, title="VMA Length")
std=input(true, title="Show Trend Direction Colors")
utp = input(false, "Use take profit?")
pr = input(100, "Take profit pips")
usl = input(false, "Use stop loss?")
sl = input(100, "Stop loss pips")
fromday = input(01, defval=01, minval=01, maxval=31, title="From Day")
frommonth = input(01, defval=01, minval= 01, maxval=12, title="From Month")
fromyear = input(2000, minval=1900, maxval=2100, title="From Year")
today = input(31, defval=01, minval=01, maxval=31, title="To Day")
tomonth = input(12, defval=12, minval=01, maxval=12, title="To Month")
toyear = input(2019, minval=1900, maxval=2100, title="To Year")
use_date = (time > timestamp(fromyear, frommonth, fromday, 00, 00) and time < timestamp(toyear, tomonth, today, 00, 00))
k = 1.0/l
pdm = 0.0
pdm := max((src - src[1]), 0)
mdm = 0.0
mdm := max((src[1] - src), 0)
pdmS = 0.0
pdmS := ((1 - k)*nz(pdmS[1]) + k*pdm)
mdmS = 0.0
mdmS := ((1 - k)*nz(mdmS[1]) + k*mdm)
s = pdmS + mdmS
pdi = pdmS/s
mdi = mdmS/s
pdiS = 0.0
pdiS := ((1 - k)*nz(pdiS[1]) + k*pdi)
mdiS = 0.0
mdiS := ((1 - k)*nz(mdiS[1]) + k*mdi)
d = abs(pdiS - mdiS)
s1 = pdiS + mdiS
iS = 0.0
iS := ((1 - k)*nz(iS[1]) + k*d/s1)
hhv = highest(iS, l)
llv = lowest(iS, l)
d1 = hhv - llv
vI = (iS - llv)/d1
vma = 0.0
vma := (1 - k*vI)*nz(vma[1]) + k*vI*src
vmaC=(vma > vma[1]) ? color.lime : (vma<vma[1]) ? color.red : (vma==vma[1]) ? color.yellow : na
plot(vma, color=std?vmaC:color.white, linewidth=3, title="VMA")
longCondition = vma > vma[1]
if (longCondition)
strategy.entry("BUY", strategy.long and use_date)
shortCondition = vma < vma[1]
if (shortCondition)
strategy.entry("SELL", strategy.short and use_date)
if (utp and not usl)
strategy.exit("TP", "BUY", profit = pr)
strategy.exit("TP", "SELL", profit = pr)
if (usl and not utp)
strategy.exit("SL", "BUY", loss = sl)
strategy.exit("SL", "SELL", loss = sl)
if (usl and utp)
strategy.exit("TP/SL", "BUY", loss = sl, profit = pr)
strategy.exit("TP/SL", "SELL", loss = sl, profit = pr)
Detail
https://www.fmz.com/strategy/442347
Last Modified
2024-02-21 11:47:43