Name
P-Signal多时间框架交易策略P-Signal-Multi-Timeframe-Trading-Strategy
Author
ChaoZhang
Strategy Description
[trans]
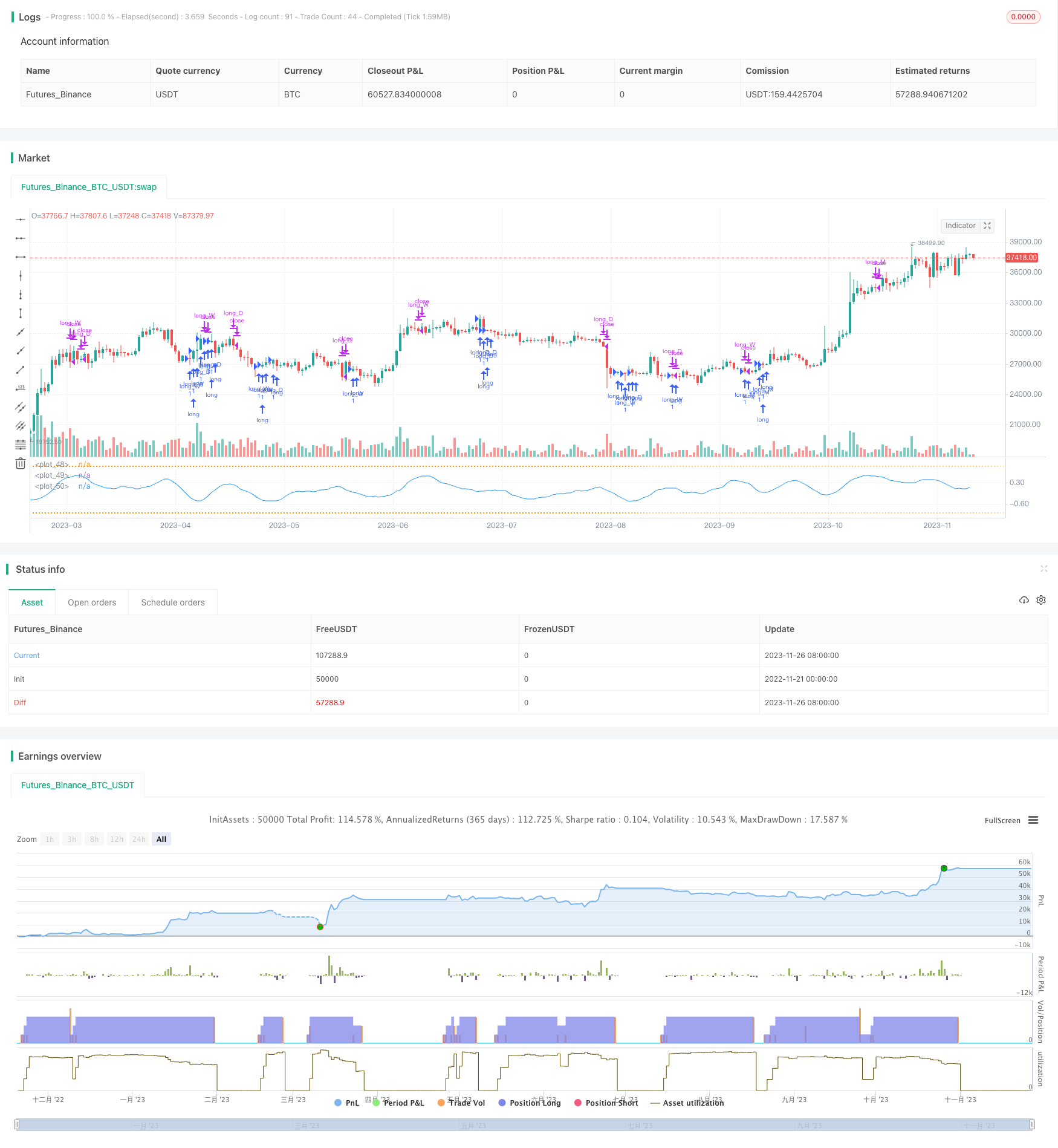
P-Signal多时间框架交易策略是一种基于统计原理,结合多时间框架分析的数字货币算法交易策略。该策略运用高斯误差函数以及P-Signal指标对比特币的日线、周线和月线进行模型fit,根据指标金叉做多和死叉做空,实现波动率交易。
P-Signal策略的核心指标是P-Signal,它结合了统计标准差和简单移动平均,通过高斯误差函数映射到-1到1区间,用来检测市场是否符合正态分布。具体计算公式如下:
fErf(x) = 1.0 - 1.0/(1.0 + 0.5*abs(x)) * exp(-x*x - 1.26551223 + ...) # 高斯误差函数
fPSignal(ser, n) = fErf((stdev(ser, n) > 0 ? sma(ser, n)/stdev(ser, n)/sqrt(2) : 1)) # P-Signal指标
该策略在日线、周线和月线时间框架分别计算P-Signal指标,当指标上穿0轴时做多,下穿0轴时平仓。同时设置指标值阀门控制重复开仓。
P-Signal策略最大的优势是利用多时间框架提高策略稳定性。日线捕捉市场短期波动,周月线过滤假突破。同时,P-Signal指标本身也具有一定的预测能力,可以放大趋势性行情的波动。
相比单一时间框架,多时间框架可以在回撤时利用日线止损,而在震荡行情中利用高级时间框架减少交易频率。整体来说,这种组合可以在保证盈利的同时最大限度降低绝对和相对回撤。
P-Signal策略最大的风险在于指标本身对量化交易员来说是一个黑箱。我们很难确定该指标对特定市场的适配度,也无法确定其参数的最优化范围。这可能导致在实盘中策略表现不佳。
此外,策略本身也存在一定的局限性。例如无法处理剧烈行情,指标差值作为交易信号可能滞后等。这些问题都可能成为实盘时的隐患。
要解决这些问题,我们可以调整指标参数,优化止损方式,引入更多辅助指标等。但前提是要在足够大的回测区间验证策略稳定性。
P-Signal策略有几个可以优化的方向:
-
更换P-Signal指标的参数:nIntr_D、nIntr_W和nIntr_M,找到最优参数组合
-
增加止损方式:跟踪止损、时间止损、ATR止损等,找到最优止损方式
-
引入辅助指标:增强策略对特定行情的判断能力,例如引入MACD判断趋势
-
优化仓位管理:设置动态仓位,优化资金使用效率
-
机器学习优化参数:使用神经网络、遗传算法等寻找参数全局最优
P-Signal多时间框架交易策略整体来说是一个非常有潜力的策略思路。它结合统计原理与技术指标,利用多时间框架分析提高稳定性。如果我们能够通过大量回测和优化解决部分局限性,完全有可能将其转化为真实可用的数字货币算法交易策略。 ||
The P-Signal multi timeframe trading strategy is a cryptocurrency algorithmic trading strategy based on statistical principles and multi timeframe analysis. The strategy uses the Gaussian error function and P-Signal indicator to model fit Bitcoin's daily, weekly and monthly charts, and goes long on indicator crosses above 0 and exits on crosses below 0, in order to trade volatility.
The core indicator of the P-Signal strategy is the P-Signal itself, which combines statistical standard deviation and simple moving average, and maps it to the -1 to 1 range using the Gaussian error function, to detect whether the market conforms to the normal distribution. The specific calculation formula is as follows:
fErf(x) = 1.0 - 1.0/(1.0 + 0.5*abs(x)) * exp(-x*x - 1.26551223 + ...) # Gaussian error function
fPSignal(ser, n) = fErf((stdev(ser, n) > 0 ? sma(ser, n)/stdev(ser, n)/sqrt(2) : 1)) # P-Signal indicator
The strategy calculates the P-Signal indicator on the daily, weekly and monthly timeframes for Bitcoin, goes long when the indicator crosses above 0, and exits when it crosses back below 0. Indicator value valves are also set to control repeated entries.
The biggest advantage of the P-Signal strategy is the use of multiple timeframes to improve strategy stability. The daily chart captures short-term market fluctuations, while the weekly and monthly charts filter false breakouts. At the same time, the P-Signal indicator itself also has some predictive capability to amplify the fluctuations of trending moves.
Compared to a single timeframe, multiple timeframes allow the use of daily stops to control drawdown during volatile times, while reducing transaction frequency using the higher timeframes during ranging markets. Overall, this combination allows maximizing profits while minimizing both absolute and relative drawdowns.
The biggest risk of the P-Signal strategy is that the indicator itself is a black box to quant traders. We have no way of determining the adaptability of this indicator to specific markets, nor can we determine the optimal range of its parameters. This may lead to poor performance of the strategy in live trading.
In addition, the strategy itself has some limitations. For example, inability to handle violent moves, lagging signal from indicator crossover etc. All these can become hidden troubles during live trading.
To solve these issues, we can adjust indicator parameters, optimize stop loss, introduce more auxiliary indicators etc. But the premise is to test stability across large enough backtesting periods.
There are several directions to optimize the P-Signal strategy:
-
Change P-Signal indicator parameters: nIntr_D, nIntr_W and nIntr_M, find optimal parameter combinations
-
Add stop loss methods: trailing stop loss, time stop loss, ATR stop loss etc, find optimal stop loss
-
Introduce auxiliary indicators: improve judgment of specific market conditions, e.g. use MACD to determine trends
-
Optimize position sizing: set dynamic position sizing based on account usage efficiency
-
Machine learning optimization: use neural networks, genetic algorithms to find globally optimal parameters
The P-Signal multi timeframe trading strategy is overall a very promising strategy idea. It combines statistical principles and technical indicators, and uses multi timeframe analysis to improve stability. If we can solve some limitations through extensive backtesting and optimization, it is entirely possible to transform it into a real, usable cryptocurrency algorithmic trading strategy.
[/trans]
Strategy Arguments
| Argument | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| v_input_1 | 9 | (?Parameters of observation.)Number of D Bars |
| v_input_2 | 4 | Number of W Bars |
| v_input_3 | 6 | Number of M Bars |
Source (PineScript)
/*backtest
start: 2022-11-21 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-27 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// **********************************************************************************************************
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// P-Signal Strategy © Kharevsky
// A good strategy should be able to handle backtesting.
// @version=4
// **********************************************************************************************************
strategy("P-Signal Strategy:", precision = 3, pyramiding = 3)
//
// Parameters and const of P-Signal.
//
nPoints_D = input(title = "Number of D Bars", type = input.integer, defval = 9, minval = 4, maxval = 100, group = "Parameters of observation.")
nPoints_W = input(title = "Number of W Bars", type = input.integer, defval = 4, minval = 4, maxval = 100, group = "Parameters of observation.")
nPoints_M = input(title = "Number of M Bars", type = input.integer, defval = 6, minval = 4, maxval = 100, group = "Parameters of observation.")
int nIntr_D = nPoints_D - 1
int nIntr_W = nPoints_W - 1
int nIntr_M = nPoints_M - 1
bool bDValveOpen = true
bool bWValveOpen = true
bool bMValveOpen = true
//
// Horner's method for the error (Gauss) & P-Signal functions.
//
fErf(x) =>
nT = 1.0/(1.0 + 0.5*abs(x))
nAns = 1.0 - nT*exp(-x*x - 1.26551223 +
nT*( 1.00002368 + nT*( 0.37409196 + nT*( 0.09678418 +
nT*(-0.18628806 + nT*( 0.27886807 + nT*(-1.13520398 +
nT*( 1.48851587 + nT*(-0.82215223 + nT*( 0.17087277 ))))))))))
x >= 0 ? nAns : -nAns
fPSignal(ser, int) =>
nStDev = stdev(ser, int)
nSma = sma(ser, int)
fErf(nStDev > 0 ? nSma/nStDev/sqrt(2) : 1.0)
//
// Signals for the strategy.
//
float nPSignal_D = sma(fPSignal(change(ohlc4), nIntr_D), nIntr_D)
float ndPSignal_D = sign(nPSignal_D[0] - nPSignal_D[1])
//
float nPSignal_W = sma(security(syminfo.tickerid, "W",fPSignal(change(ohlc4), nIntr_W)), nIntr_W)
float ndPSignal_W = sign(nPSignal_W[0] - nPSignal_W[1])
//
float nPSignal_M = sma(security(syminfo.tickerid, "M",fPSignal(change(ohlc4), nIntr_M)), nIntr_M)
float ndPSignal_M = sign(nPSignal_M[0] - nPSignal_M[1])
//
// P-Signal plotting.
//
hline(+1.0, color = color.new(color.orange,70), linestyle = hline.style_dotted)
hline(-1.0, color = color.new(color.orange,70), linestyle = hline.style_dotted)
plot(nPSignal_D, color = color.blue, style = plot.style_line)
//
// Multi Frame Strategy
// ... Day
if(nPSignal_D < 0 and ndPSignal_D > 0 and bDValveOpen)
strategy.entry("long_D", strategy.long, 1)
bDValveOpen := false
if(nPSignal_D > 0 and ndPSignal_D < 0)
strategy.close("long_D")
bDValveOpen := true
// ... Week
if(nPSignal_W < 0 and ndPSignal_W > 0 and bWValveOpen)
strategy.entry("long_W", strategy.long, 1)
bWValveOpen := false
if(nPSignal_W > 0 and ndPSignal_W < 0)
strategy.close("long_W")
bWValveOpen := true
// ... Month
if(nPSignal_M < 0 and ndPSignal_M > 0 and bMValveOpen)
strategy.entry("long_M", strategy.long, 1)
bMValveOpen := false
if(nPSignal_M > 0 and ndPSignal_M < 0)
strategy.close("long_M")
bMValveOpen := true
// The end.
Detail
https://www.fmz.com/strategy/433581
Last Modified
2023-11-28 16:32:36