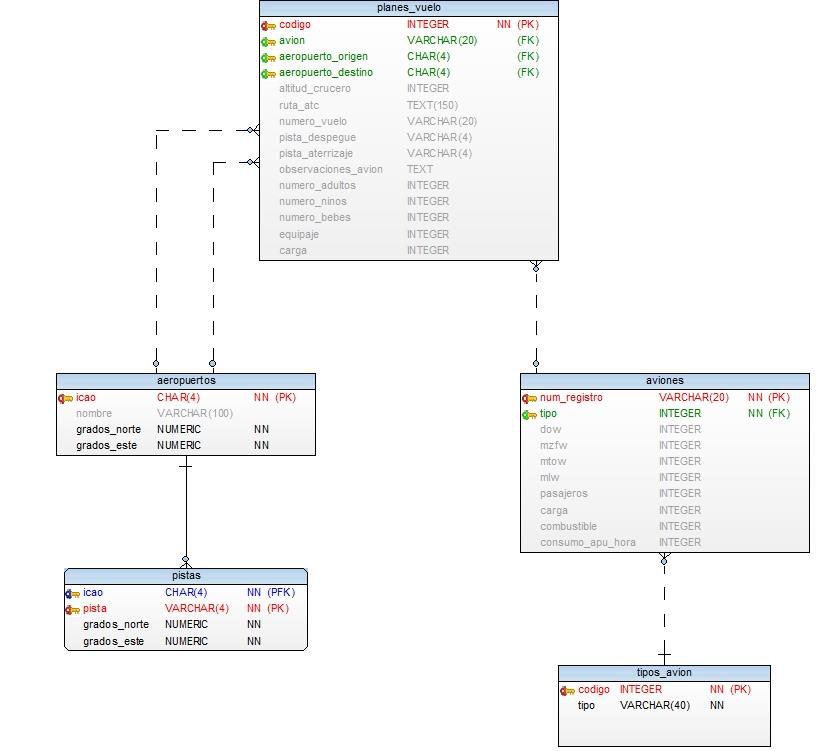
Due to the high technical content of this application it is necessary to clarify some concepts before proceeding to the presentation of it.
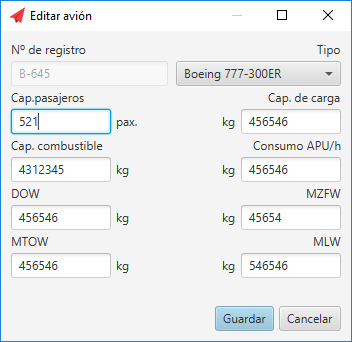
- DOW: The empty weight of the airplane (to simplify we will use kilograms as a weight unit, it is common to use pounds or gallons in the case of fuel).
- MZFW: The maximum weight of the plane without any fuel.
- MTOW: The maximum takeoff weight.
- MLW: The maximum landing weight.
- Cruising Altitude: The altitude (in feets) that the airplane will maintain along its route, the nomenclature used to define the cruising altitude consists of prefixing FL (Flight Level) in front of the first 3 numbers of the cruise. (for example, to define a cruising altitude of 37000 feets, FL370 would be used).
- ICAO: Code of 4 alphanumeric characters that identifies a specific airport in the world (for example, London Heathrow has the ICAO code: EGLL).
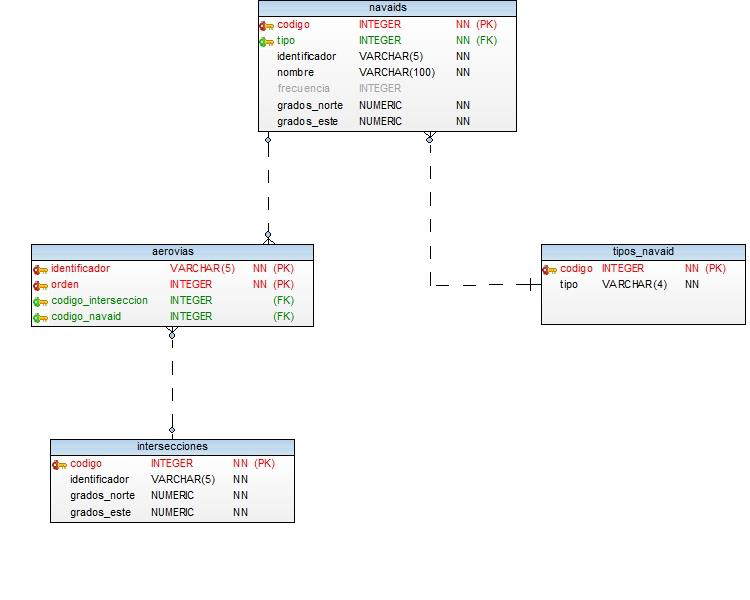
- Intersection: It is a point on the terrestrial surface determined by its geographic coordinates that usually coincide with the crossing between two or more airways or between airways and airspace limits, they are identified by a 5-character alphanumeric code (for example, the intersection DEVIS is at latitude -51.0552, length -70.4972, approximately).
- Navaid: They are navigation aids, they are divided into many types (although to simplify only 6 types are used) and are usually identified by an alphanumeric code between 1 and 4 characters:
- VOR: It is an omnidirectional VHF radio beacon, it is a radio navigation aid used by aircraft to follow a pre-established route in flight. There is usually a land VOR station at each airport, as well as others in route.
- NDB: It is a non-directional beacon, a radio transmitter located in a known place, used as an aid for air or sea navigation as a radio beacon. As its name implies, the transmitted signal does not include inherent directional information, in contrast to other navigation aids such as LFR, VOR and TACAN.
- ILS: The instrumental landing system (ILS) is an approach and landing aid system. This control system allows an aircraft to be guided with precision during the approach to the runway and, in some cases, land the plane automatically.
- DME: It is a distance measuring device, an electronic system that allows to establish the distance between it and a transmitting station, replacing the radio beacons in many facilities.
- VORD: It's a VOR to which a DME has been added.
- ILSD: It is an ILS to which a DME has been added.
- Airway: Union of intersections and navaids (except ILS and ILSD) that defines an air route through which airplanes must circulate, are identified by an alphanumeric code that usually begins with one or more letters and ends with one or more numbers (for example, the UM30 airway passes through the intersection PARKA and ZORBA).
- DCT: It is simply an abbreviation of "direct", it is used in the ATC routes to indicate that no airway will be followed to travel between two intersections or navaids, normally it is tried to avoid its use.
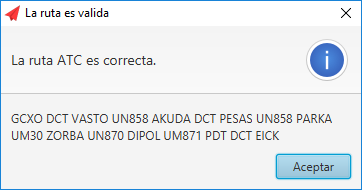
- ATC Route: Sequence of codes that indicates which route an airplane will follow from the departure airport to the arrival airport, it has the following format:
[DEPARTURE ICAO] [SID] ... [AIRWAY or DCT] [INTERSECTION or NAVAID (except ILS and ILSD)] ... [STAR] [ARRIVAL ICAO]
In this case and to simplify the SID (Standard Instrumental Departure) or the STAR (Standard Terminal Arrival Route) will not be taken into account, other common formats to represent an ATC route will not be taken into account. An example of an ATC route from Los Rodeos airport in Tenerife to Adolfo Suarez airport in Madrid would be the following:
GCXO DCT VASTO UN858 AKUDA DCT WEIGHTS UN858 PARKA UM30 ZORBA UN870 DIPOL UM871 PDT DCT LEMD
- APU: Auxiliary power unit, is an electric combustion generator that most aircraft have to provide power to navigation systems when the engines are off.
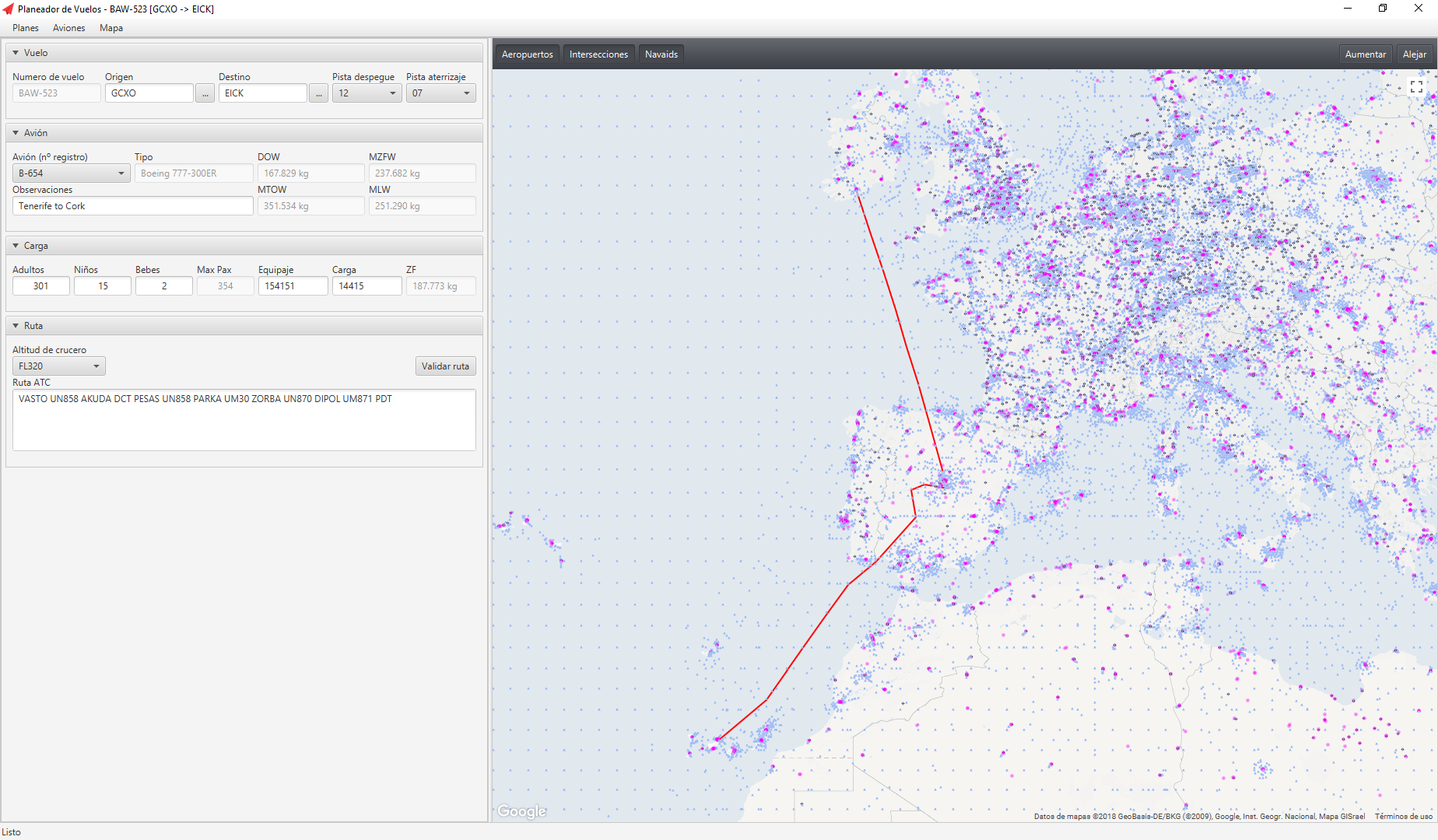
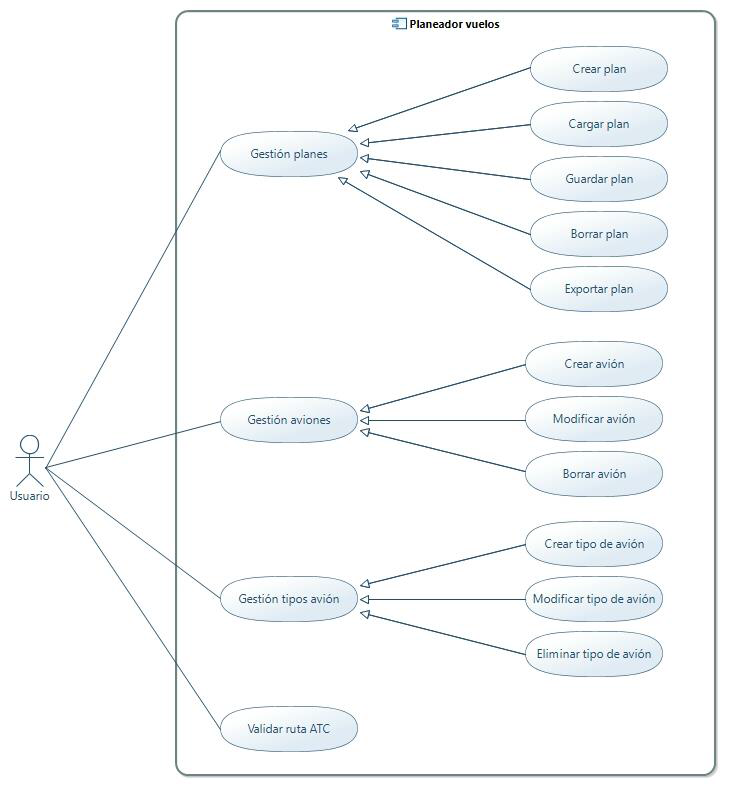
Flight Planner is a desktop application for the management of flight plans and aircrafts that has a graphical user interface to visualize the route and facilitate planning tasks.
This software is focused on aviation professionals (pilots and airlines) and flight simulation enthusiasts and the application uses the AIRAC 1502 cycle of the company Navigraph (previous authorization of the same) to provide all the necessary data for the creation of a flight plan (airports, intersections, navaids and routes all around the globe).
- Management of flight plans (creation, modification and deletion).
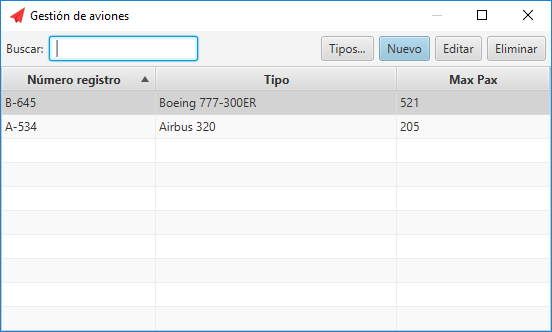
- Management of aircraft and types of aircraft.
- Validation of ATC routes.
- Basic simulation of cargo.
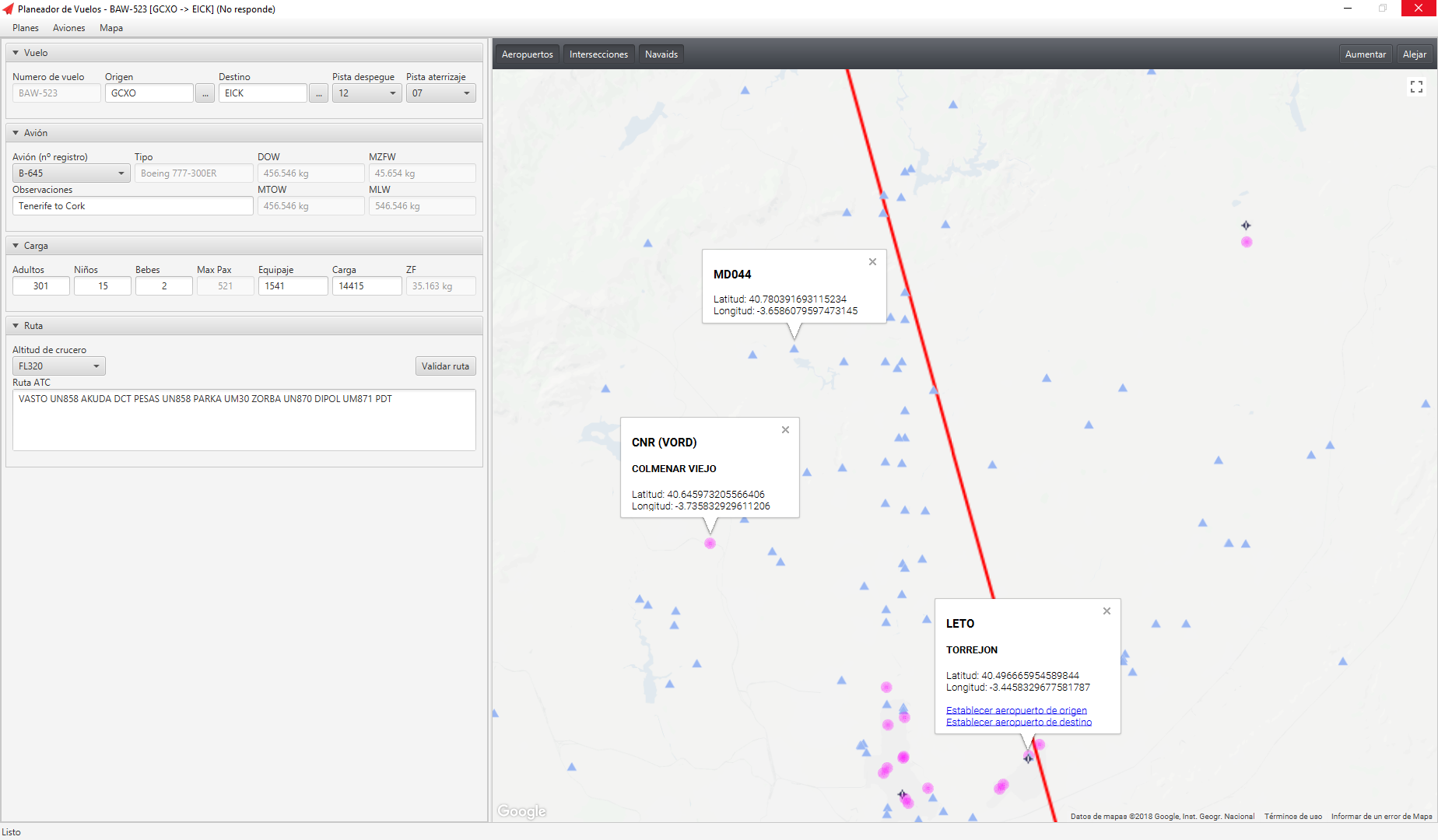
- Visualization of navigation data and route in a map.
- The possibility of exporting the flight plan to PDF format.
-
Principal view
-
Map
-
Airport selection
-
Airplane selection
-
Edit airplane
-
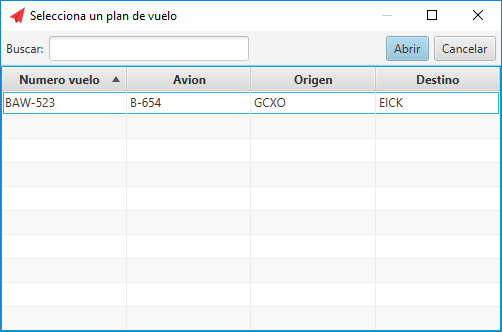
Flight plan selection
-
Validation of ATC route
MIT