This toolbox contains a custom version of the CPF toolbox for MatPower, a Matlab - based power system simulation toolbox. I am adding features to this toolbox in order to evaluate solvability of systems.
Changes so far:
- Implemented participation factors.
- Extended to scaling of all loads instead of just one load.
- Implemented Lagrange Polynomial interpolation for prediction step to improve accuracy and speed of predictions.
- Implemented variable step sizes to improve speed for relatively flat sections.
The CPF algorithm is a method for determining PV curves on a bus; it uses a formulation that allows for the Newton-Raphson power flow algorithm to converge right up to the limit of solvability.
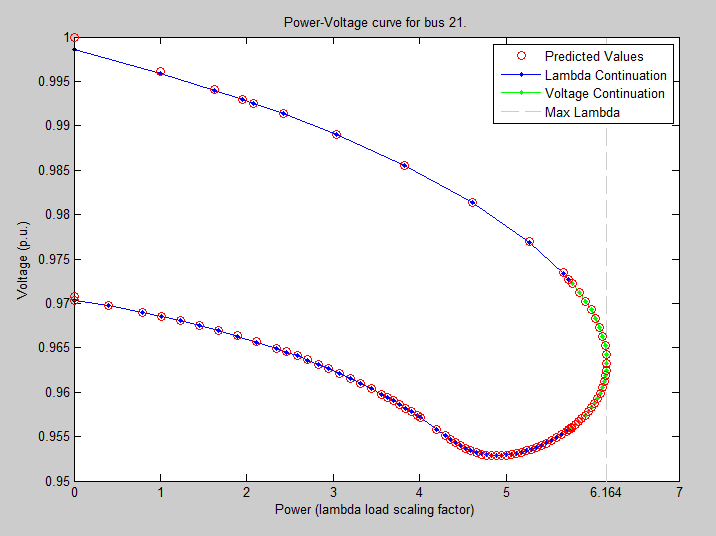
Below is a sample PV curve for a single bus, showing the CPF algorithm. The red circles show the predicted solutions for a given step in lambda (when lambda is the continuation parameter; alternatively, for a given step in voltage). The blue (and green) dots show the solutions from the correction step, which uses the prediction values and continuation parameter as a starting value for solving Newton-Raphson. The green segement of the curve denotes that in this phase a bus voltage is used as the continuation parameter (as opposed to the power scaling factor lambda) in order to slowly traverse the nose of the PV curve without taking steps that are too large. Although this graph shows only one bus, in fact all of the PV buses on the network can participate in the scaling of load.
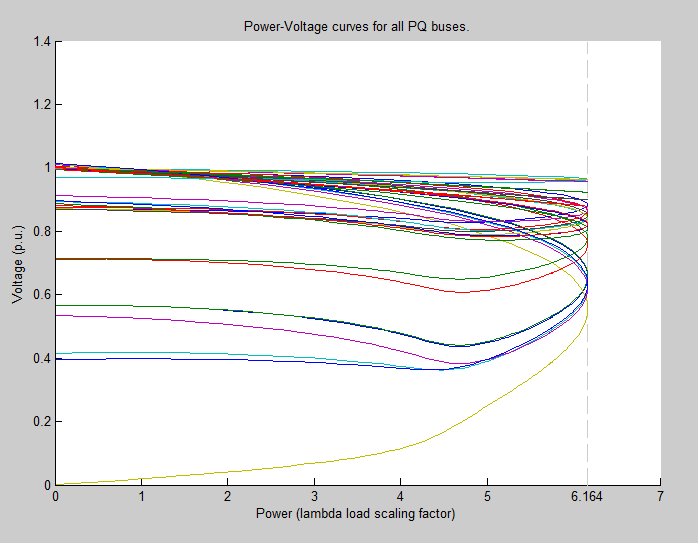
Below is a graph superimposing the PV curves for all the buses on one axis.