Optimizes DNA sequences for cloning by lowering the GC content through codon optimization, while avoiding reducing the codon frequencies.
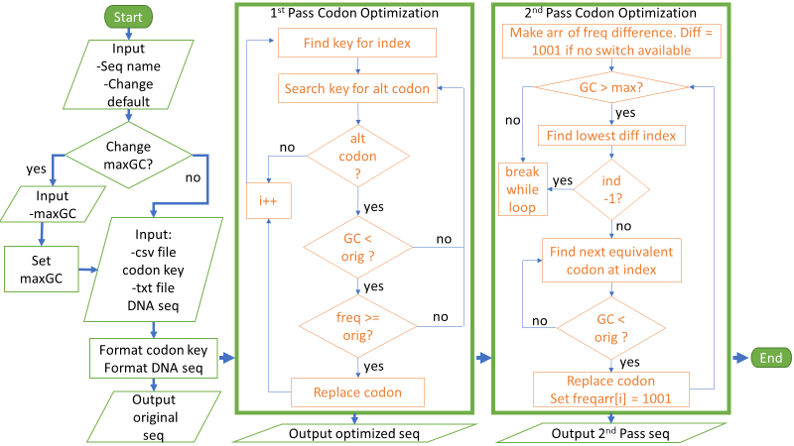
DNA sequences go through either one or two passes depending on the input sequence and the parameters. The first pass optimization only changes codons if there is an alternate codon that has a lower GC% and an equal or higher frequency. If it is impossible to lower the GC content of the sequence without lowering the frequency, then a second pass optimization will occur. The second pass optimization determines the reduction in frequency of the next best codon at each index of the sequence and replaces the codons starting at the smallest frequency difference until the sequence meets the GC parameter.
Program outputs the original sequence, the first pass optimized sequence, and the second pass optimized sequence. When aligned in a software like JalView the differences in DNA sequence can be seen but the protein sequences are identical.
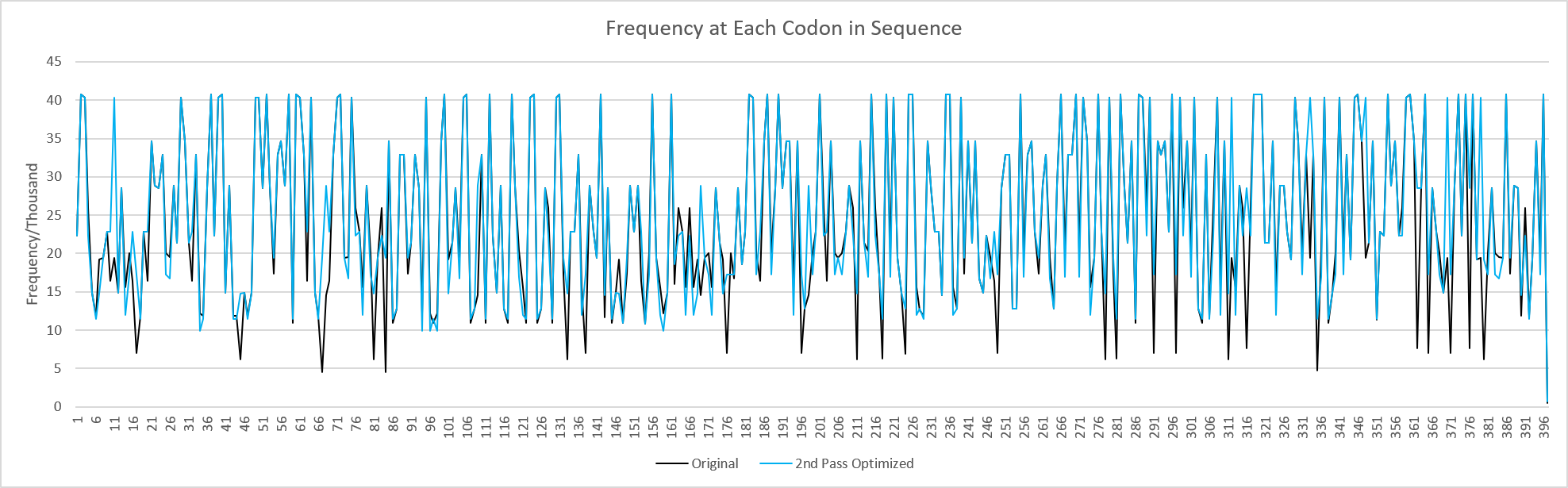
Since the first pass optimization increases frequency of codons, when the second pass opimization lowers frequency to reduce GC content, the final sequence can have a higher frequency than the original.
- Input CSV key should have codons ordered from highest frequency to lowest.
- Input sequence file should only contain sequence without name
- User can set GC% but some percentages may be impossible for the sequence. In that case, program will output a warning message.