PumpkinPal is an open-source app that helps competitive pumpkin growers enter and track their pumpkin-growing journey. This app is in development. Feel free to visit the live app at pumpkinpal.app.
The goal of this project is to develop a user-friendly, open-source application for competitive pumpkin growers. The app's primary users are hobbyists in the giant pumpkin growing community.
Our mission is to empower the pumpkin growing community by providing a tool that makes the hobby more accessible and enjoyable. We envision a future where every weigh-off is crowded with more and heavier pumpkins, and we're committed to making that vision a reality through the continuous development and improvement of PumpkinPal.
PumpkinPal is committed to remaining free for all users. We believe in the power of community and the spirit of sharing knowledge and resources. As such, we pledge to keep PumpkinPal free to use, now and always.
-
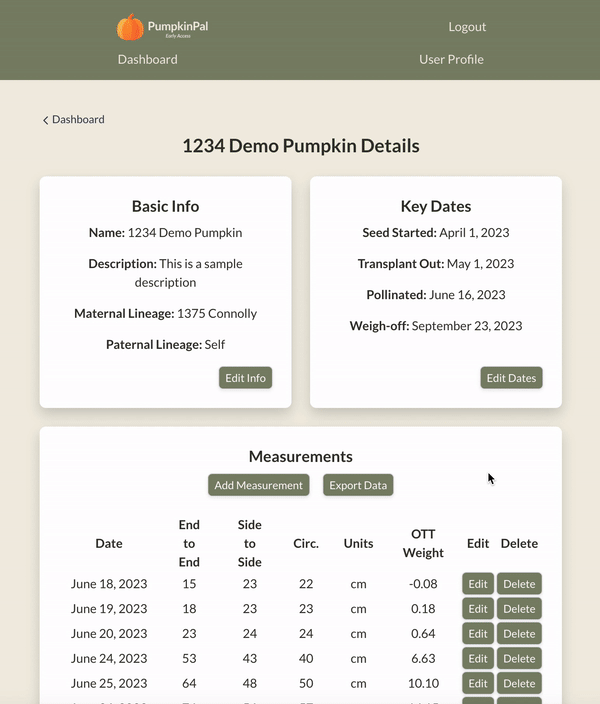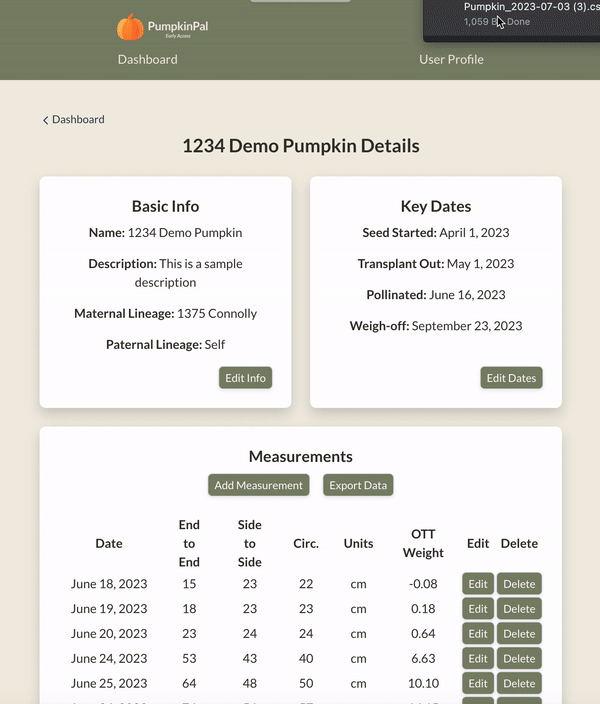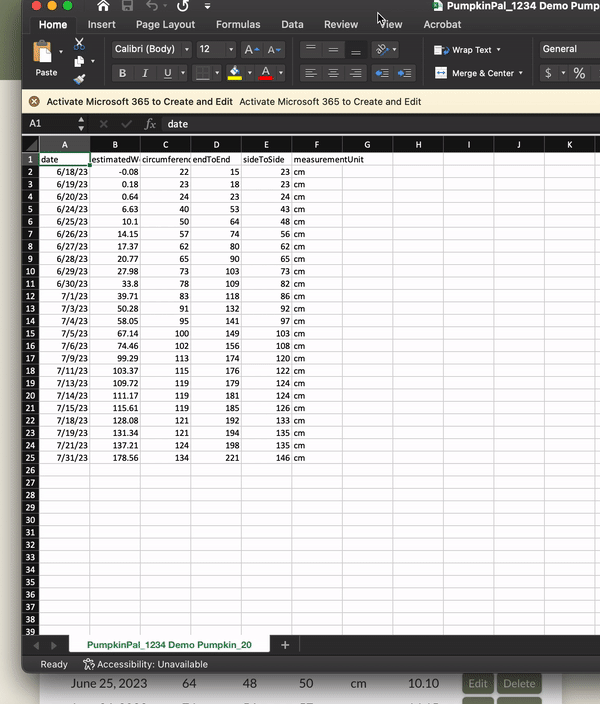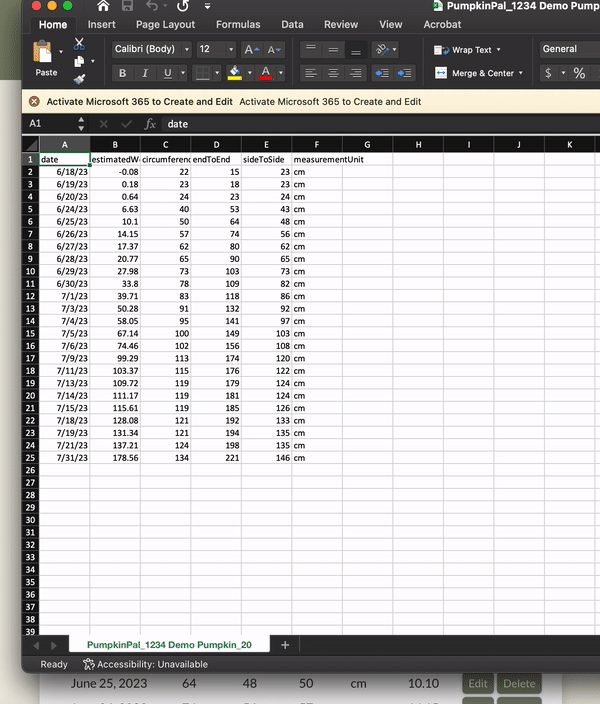
Pumpkin Dashboard: The Pumpkin Dashboard is a central hub for growers to track all their growing pumpkins. It provides a comprehensive overview of each pumpkin's progress, making it easy to monitor and compare growth trends.
-
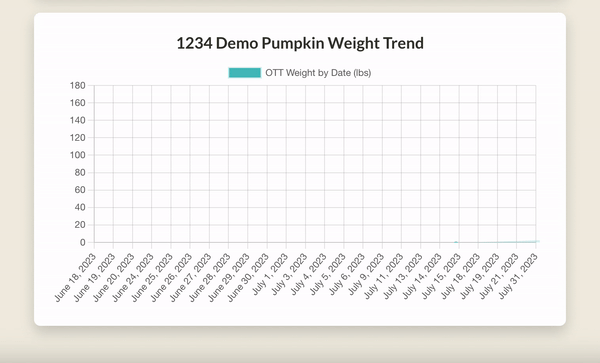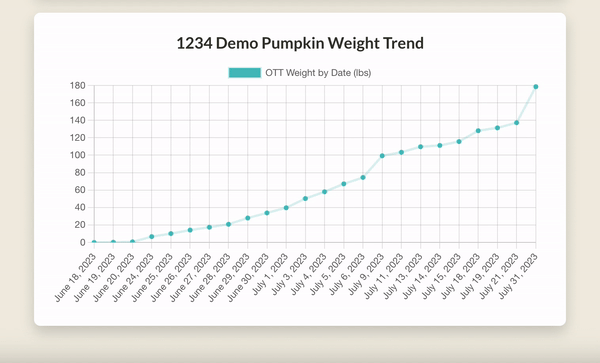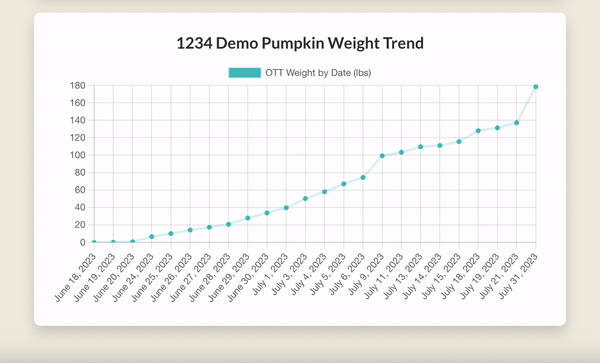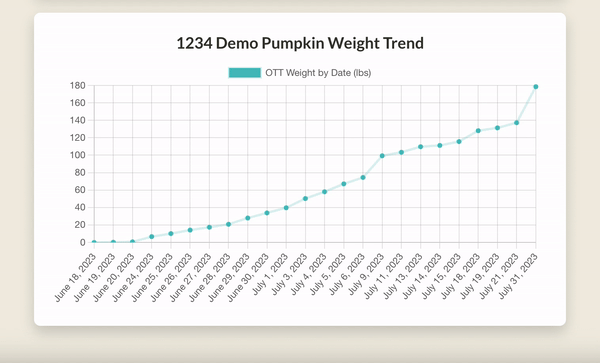
OTT Weight Calculation & Tracking: The OTT Weight Calculation feature allows for in-field estimation of pumpkin weight using the Over The Top (OTT) formula. Beyond simple calculation, the app tracks these measurements over time, providing a visual graph of each pumpkin's growth trend. This feature not only gives an instant weight estimate but also allows growers to monitor their pumpkin's development over the growing season.
-
Image Gallery: Growers can take photos with the app or upload them, associating each image with the relevant pumpkin and its stats like DAP and date. Users can also share their images directly to Facebook using the Facebook SDK.
-
PumpkinPal Database: The custom-built PumpkinPal Database is the backbone of the app. It enables the calculation of rankings and stats for growers, pumpkins, and GPC sites. Leveraging AI technology, the database cleans all available GPC results from BigPumpkins.com, creating the most comprehensive pumpkin database ever built.
-
Weigh-Off Stats: The Weigh-Off Stats feature provides a personal grower profile for users who have competed in GPC sanctioned weigh-offs. Users can see all their stats from rankings to results, providing a detailed overview of their performance.
-
GPC Search: The GPC Search feature enables users to find any grower, pumpkin, or site and see a comprehensive overview, rankings, stats, etc. This powerful tool makes it easy to find specific information within the app, providing a seamless user experience.
-
User Data Export: Users can export their data for further analysis or record-keeping, ensuring they can use it outside the app in whatever way they find most useful.
- React.js: The backbone of the application, providing a robust framework for building the user interface.
- Tailwind CSS: A utility-first CSS framework used for styling the application.
- Firebase: Used for user authentication and real-time database management.
- React Router Dom: This is a standard routing library for React, used to navigate between different components, enhancing the single-page application experience.
- React Hot Toast: This lightweight notification library for React apps is used to provide customizable toast notifications to the user, improving user feedback and interaction.
- React Firebase Hooks: This library provides a set of reusable React hooks for Firebase, making it easier to interact with Firebase database.
- React Modal: This library offers a simple way to implement React-based modals. It is used for creating the image gallery feature in the app.
- React Table: This library is used for building fast and extendable tables and datagrids for React, used in displaying the weigh-off stats.
- Axios: This promise-based HTTP client is used for making API requests.
- AlgoliaSearch: This library is used to enable the instant search feature in the app, providing a seamless user experience.
- Moment: This library is used to manipulate dates and times in JavaScript, used in tracking and displaying the growth of pumpkins over time.
- React Chartjs 2: A wrapper for Chart.js, this library is used for creating dynamic and interactive data visualizations in the app, making it easier for users to understand their pumpkin growth trends.
I opted to develop this app in React because I believe React is the best framework for coding with AI assistance using tools like ChatGPT or Cursor, which leverages GPT-4 via OpenAI's API. React's popularity, component-based architecture, and existing integrations make it an ideal choice for coding with AI agents.
-
Popularity: React.js is one of the most popular JavaScript libraries, with a large community of developers and a wealth of resources. This popularity means that LLMs have a vast amount of training data relating to React, helping generate accurate and useful responses.
-
Component-Based Architecture: React's component-based architecture is particularly suited to AI-assisted development. Components can be isolated and worked on individually, making it easier to share relevant, self-contained code with AI code assistants. This modular approach also allows for code reuse, simplifies the codebase, and fits well within the token limits and context windows of large language models (LLMs).
-
Integration with Emerging Technologies: React's large user base ensures it integrates well with other emerging technologies. This compatibility ensures that PumpkinPal can leverage these technologies to enhance its functionality and stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
I considered various options, including setting up a MERN (MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, Node.js) stack. However, I ultimately decided to streamline the process with a Backend as a Service (BaaS) provider. Firebase emerged as the clear choice for its simplicity, real-time capabilities, scalability, ease of integration, and cost-effectiveness, making it a perfect fit for a small-scale application like PumpkinPal.
-
Popularity: Firebase is a widely-used Backend as a Service (BaaS) provider, with a large community and a wealth of resources. This popularity means that AI-assisted code editors have a vast amount of training data from the internet on common Firebase-related problems, making it easier to generate accurate and useful code suggestions.
-
Scalability: Firebase is designed to handle large amounts of data and heavy user loads, ensuring the app can grow without performance issues. This scalability is crucial as the user base of the app grows, and Firebase's ability to easily accommodate the increased traffic and data is a major plus.
-
Integration with AI-assisted Code Editors: Firebase's seamless integration with React.js simplifies the connection between the frontend and backend, allowing for faster development and reducing the potential for errors. This ease of integration is particularly beneficial when working with AI tools, as it allows the AI to focus on the logic and functionality rather than the intricacies of connecting disparate systems.
-
Integration with Google's Palm LLM: Firebase's integration with Google's Palm large language model (LLM) allows for advanced natural language processing capabilities, enhancing the app's functionality and user experience.
Tailwind CSS was chosen as the styling framework for PumpkinPal due to its popularity, inline styling approach, and compatibility with AI-assisted code editors like Cursor.
-
Popularity: Tailwind CSS is a widely-used CSS framework, with a large community and a wealth of resources. This popularity means that AI-assisted code editors have a vast amount of training data from the internet on common Tailwind CSS-related problems, making it easier to generate accurate and useful code suggestions.
-
Inline Styling Approach: Tailwind CSS's inline styling approach, where styles are applied directly to HTML elements, is a game-changer for AI-assisted development. It allows the entire context, including the HTML structure and styles, to be visible in a single snippet, eliminating the need to reference separate CSS files. This approach simplifies the task for AI tools, making it easier to generate or modify styles.
-
Integration with AI-assisted Code Editors: The utility-first approach of Tailwind CSS allows for highly customizable designs without leaving your HTML. This makes it a joy to work with, especially when using AI-assisted code editors, as it allows the AI to focus on the logic and functionality rather than the intricacies of connecting disparate systems.
The application employs react-hot-toast to manage notifications and provide feedback to the user about the success or failure of various operations. This library provides a simple and intuitive API for creating toast notifications from anywhere within the application.
PumpkinPal uses Google Analytics to track errors and user events, providing valuable insights into user behavior and system performance. This tracking is implemented using the react-ga4 library, which provides a simple and efficient way to integrate Google Analytics with a React application.
The tracking logic is contained in the error-analytics.js file in the utilities directory. This file exports two main functions: trackError and trackUserEvent.
-
trackError: This function is used to send error events to Google Analytics. It takes an error object, a method name, and optionally a category and action. The category defaults to "System" and the action defaults to "Error". The function sends an event to Google Analytics with the category, action, and a label that includes the method name and error details. It also includes a dimension that indicates whether the app is running in development or production mode.
-
trackUserEvent: This function is used to send user events to Google Analytics. It takes an action and a method name, and sends an event to Google Analytics with the category "User", the provided action, and a label that includes the method name.
The GA_CATEGORIES and GA_ACTIONS objects define the categories and actions used in the tracking events. These include user actions like "Register", "Login", and "Add Pumpkin", as well as system actions like "Error".
By tracking both user events and errors, we can monitor the full user journey, from registration and login to adding and updating pumpkins. This comprehensive tracking allows us to identify which features are most used, how users navigate through the app, and where they may encounter difficulties or errors.
The use of categories and actions in the tracking events provides a structured way to analyze the data. For example, we can easily filter events by category to see all user actions or system errors, or by action to see all instances of a specific event like "Register" or "Add Pumpkin".
Furthermore, the inclusion of a dimension indicating whether the app is running in development or production mode allows us to separate testing and real user data, ensuring the accuracy of our analysis.
The error-analytics.js file in the utilities directory provides a centralized location for all tracking logic, making it easy to maintain and update as needed. The trackError and trackUserEvent functions provide a simple and consistent way to send events to Google Analytics, ensuring that all events are tracked in a consistent and reliable manner.
For more details on how to use Google Analytics with PumpkinPal, refer to the GoogleAnalyticsGuide.md file in the utilities directory.
The estimated weight of the pumpkin is calculated based on the Over-the-Top (OTT) method, which involves adding the measurements from end to end, side to side, and around the circumference of the pumpkin.
The calculation is made by first adding the three measurements together to get the OTT. The OTT value is then fed into a two-part formula that estimates the weight of the pumpkin based on various growth factors.
The first part of the formula ((14.2 / (1 + 7.3 * Math.pow(2, -(ott) / 96))) ** 3 + (ott / 51) ** 2.91) - 8 is an empirically derived relationship between OTT and pumpkin weight. The second part * 0.993 applies a slight correction factor to the weight.
If the computed weight turns out to be less than 0 (which can happen if someone measures a small/young pumpkin), we set the weight to 0. The result is then rounded to two decimal places to give a more readable weight estimate.
const calculateEstimatedWeight = (endToEnd, sideToSide, circumference, measurementUnit) => {
let ott = parseFloat(endToEnd) + parseFloat(sideToSide) + parseFloat(circumference);
if (measurementUnit === 'cm') {
ott /= 2.54; // Convert cm to inches
}
let weight = (((14.2 / (1 + 7.3 * Math.pow(2, -(ott) / 96))) ** 3 + (ott / 51) ** 2.91) - 8) * 0.993;
// If weight is less than 0, set it to 0
if (weight < 0) {
weight = 0;
}
return weight.toFixed(2); // round to 2 decimal places
};This formula is the crux of the PumpkinPal app and what enables pumpkin growers to track and predict their pumpkins' weight throughout the growing season based on their measurements.
The PumpkinPal app incorporates several design principles to ensure ease of use in a field environment, especially while wearing gloves.
-
Big inputs and touch targets: Recognizing that our users may be interacting with the app with gloves on, we've designed our input fields and touch targets to be large enough to accommodate these circumstances. This is achieved through custom CSS rules that boost the default size attributes of the HTML input elements.
-
Smart defaults for data entry: The app intelligently fetches the most recent measurement for each pumpkin from the Firebase backend and prepopulates the fields with these values whenever a new measurement is being entered. This functionality is implemented via a useEffect hook in the AddMeasurement component that triggers whenever the selectedPumpkin state changes, so the user can select any pumpkin from the dropdown to have the defaults update automatically.
-
Dynamic measurement unit selection: The app pulls the user's preferred measurement unit from Firebase and uses it as the default unit. However, the user also has the option to override this default on-the-fly for individual measurements, providing flexibility when it's needed.
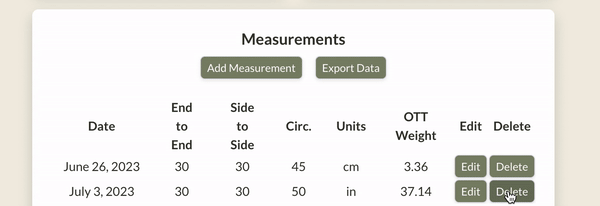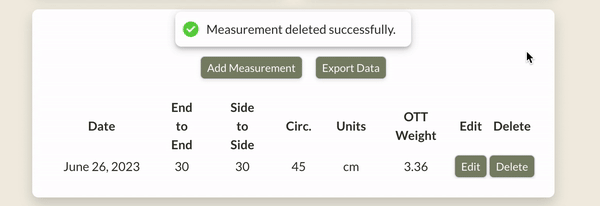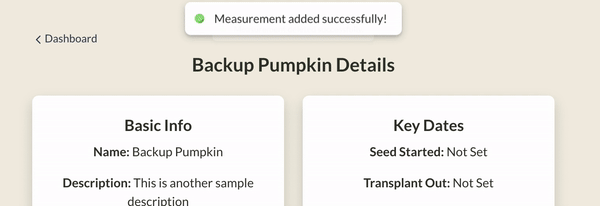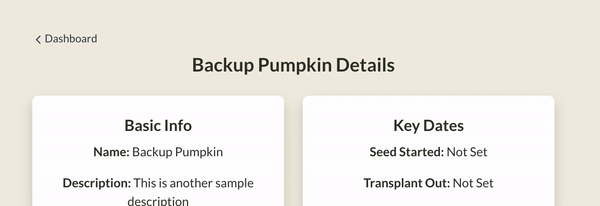
Here's what it looks like in action:
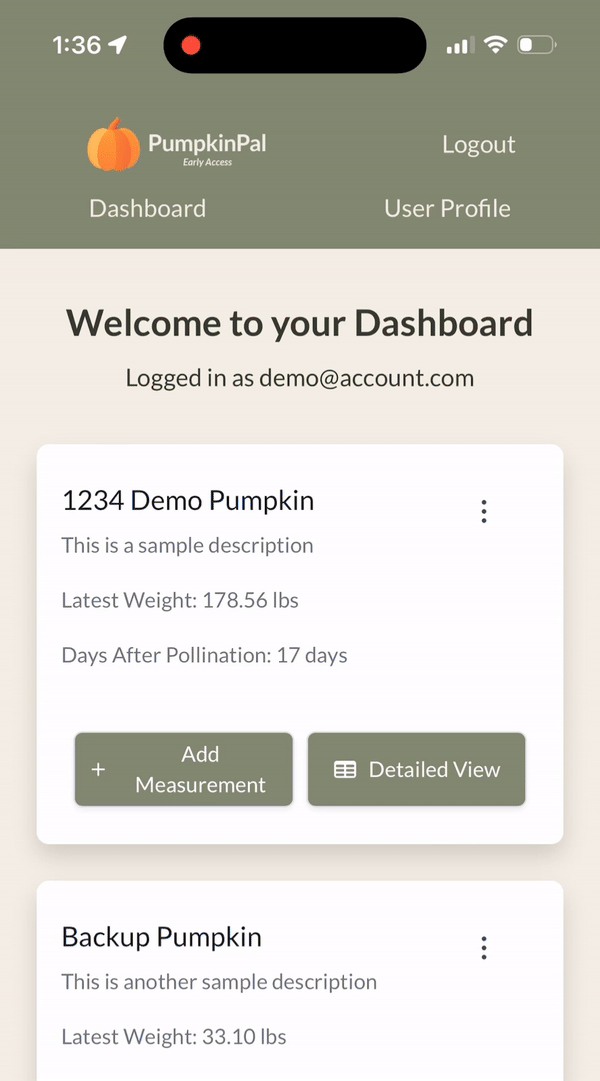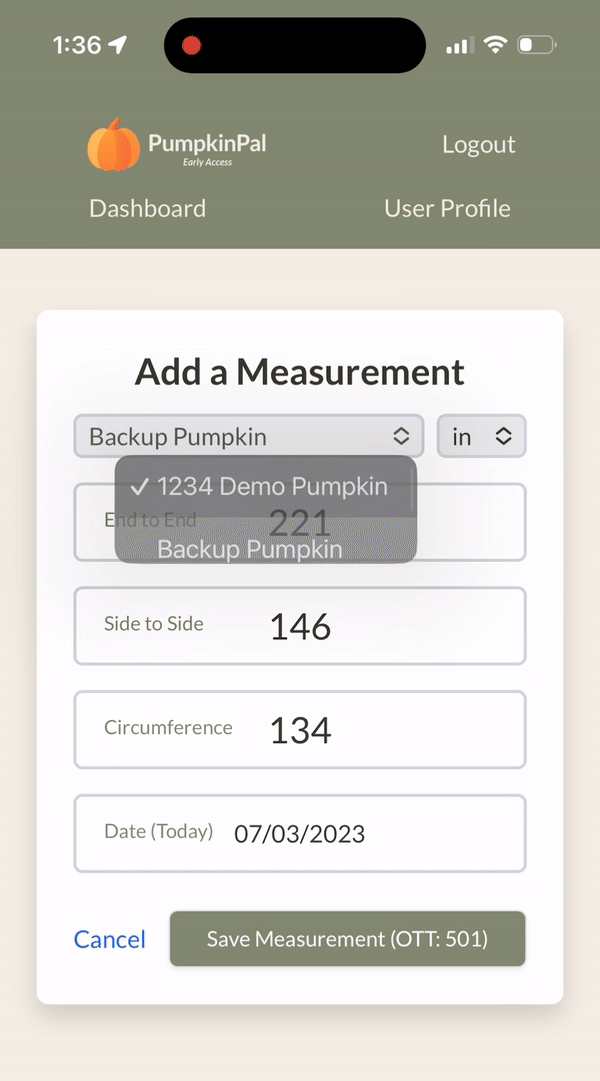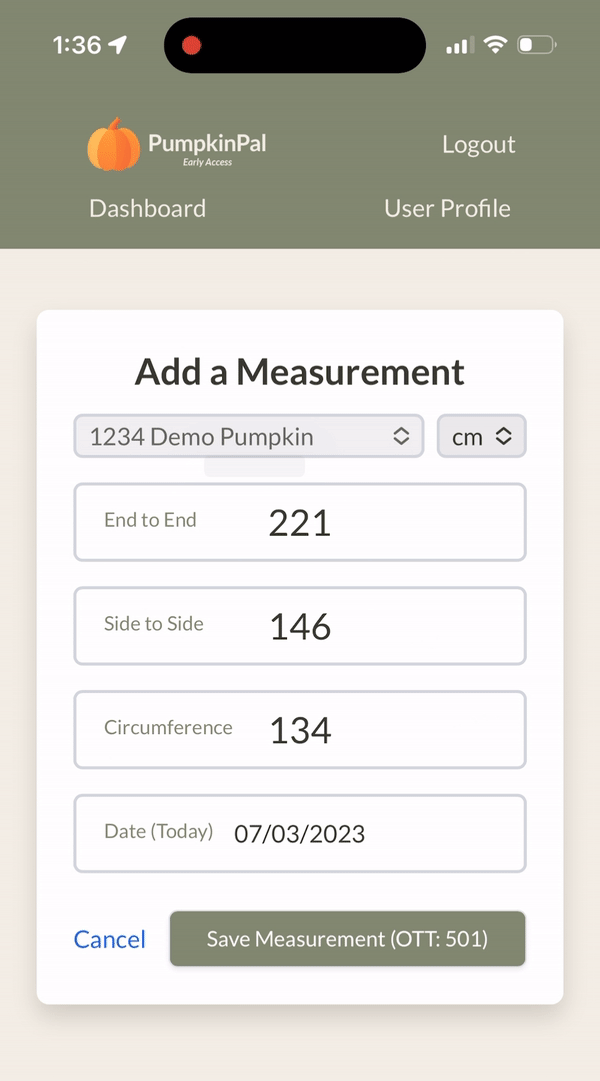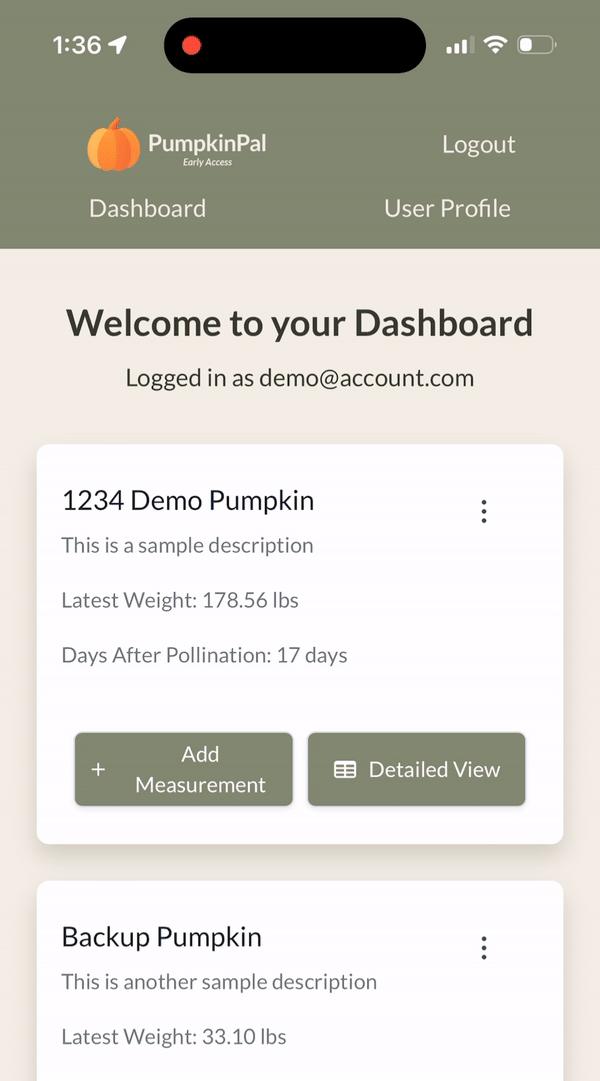
Data resilience and reliability are non-negotiable. PumpkinPal uses Google's cloud ecosystem to maintain data integrity and ensure high availability through automatic, daily snapshots of our entire Firestore backend. This mitigates potential data loss scenarios and provides swift recovery paths.
Our data backups use Google Cloud's serverless technology, enhancing scalability, and minimizing overhead. We've implemented a Cloud Function, scheduledFirestoreExport, that operates on a cron-based schedule. This function orchestrates the export of Firestore data, leveraging Firestore's built-in exportDocuments operation and pushing the data to a secure Google Cloud Storage bucket.
A Google Cloud Function, scheduledFirestoreExport, orchestrates the data export pipeline. It interfaces with Firestore's exportDocuments method, initiating a server-side operation that atomically exports Firestore documents to a designated Google Cloud Storage bucket. Here's the function:
const firestore = require('@google-cloud/firestore');
const client = new firestore.v1.FirestoreAdminClient();
const bucket = 'gs://pumpkinpal_backup'
exports.scheduledFirestoreExport = (event, context) => {
const projectId = process.env.GCLOUD_PROJECT;
const databaseName = `projects/${projectId}/databases/(default)`;
return client
.exportDocuments({
name: databaseName,
outputUriPrefix: bucket,
collectionIds: [],
})
.then(responses => {
const response = responses[0];
console.log(`Operation Name: ${response['name']}`);
return response;
})
.catch(err => {
console.error(err);
});
};The Firestore backups live in a secure Google Cloud Storage bucket. Leveraging the high durability and regional redundancy offered by Google Cloud, our data is replicated across multiple regions in the United States. This setup fortifies our data integrity, ensuring robust data durability and high availability.
The PumpkinPal application uses React's Context API for state management, providing a way to share state and functionality across components.
React's Context API is used to create global state variables that can be accessed from any component. A UserContext is created to store the current user's data and a loading state. This context is provided at the root level of the application, making it accessible to all child components.
import React, { createContext, useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { auth } from '../firebase';
export const UserContext = createContext();
export function UserProvider({ children }) {
const [user, setUser] = useState(null);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
useEffect(() => {
const unsubscribe = auth.onAuthStateChanged(user => {
setUser(user);
setLoading(false);
});
return unsubscribe;
}, []);
return (
<UserContext.Provider value={{ user, loading }}>
{children}
</UserContext.Provider>
);
}We welcome contributions from the community! If you're interested in contributing, please follow these steps:
- Fork the repository on GitHub.
- Clone your forked repository to your local machine.
- Make your changes and commit them to your forked repository.
- Submit a pull request with your changes to the main repository.
Please ensure your code adheres to our coding standards and conventions. All contributions are subject to review and approval by the project maintainers.
This project is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial (CC BY-NC) License. This means you are free to remix, adapt, and build upon this work, but not for commercial purposes. Please remember to give appropriate credit and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.